As mandated by the constitution of India, Income tax return filing is a foremost requirement by all registered taxpayers in India. Thanks to the outbreak of technology in India, the ITR filing can now be done via both Online and Offline modes.
E-filing or electronic filing is the newly inaugurated process for filing online Income tax returns and the write-up is aimed at giving you the complete information of the e-filing ITR process, its significance, eligibility, deadline and so on.
- Process for E-filing of ITR Electronically
- Eligibility for Income Tax Return Filing
- Deadline for ITR Filing
- E-filing with Form 16
- E-filing without Form 16
- In case if I lost IT E-filing Password
- Income Tax Return Filing FAQ’s
Latest Update
- Recent tweets from the Income Tax Department warned taxpayers of fake accounts posing as customer service and helplines. Twitter user @incomet67691294 replied to an official tweet from the Income Tax Department with a tweet from a fake account.
- Most important FAQs related to income tax filing, self-assessment, pre-validate, e-verify, changing tax regimes, etc. are mentioned by the department via a PDF file. read more
- The Income-tax department has introduced an e-brochure to help individuals to file their first tax return. Check PDF
- “The Income-tax department has showcased the database of total income tax returns. Above 3.59 crores Income tax returns have filed on portal till 15th December and per day average is more than 6 lakh.” Read Press Release
- “The Income-tax department has released the press release regarding the extension of due dates for filing ITR forms, Tax Audit Reports, etc under the Income-tax Act, 1961.” Read Press Release
Definition of e-filing
E-filing is the process of electronically furnishing the returns of the taxes paid by you. The government allows both Online and Offline Income Tax Return (ITR) filing, whichever is convenient for the taxpayer. However, E-filing or electronic ITR Filing has overtaken the traditional offline method as many taxpayers find it convenient to file the returns from their offices without much paperwork. Above all e-filing is free of cost procedure.
Process for E-filing of ITR Electronically:
- Tax Calculations – Firstly the taxpayer needs to make the exact calculation of his taxable income in line with the current tax norms applicable to him. Here Calculate your free Income Tax
- Filing the Right Form – The taxpayer needs to file the form as per his/her source of income. There are different ITR forms available depending upon their source of income and status of taxpayers like income from a business, employment, LTCG, TDS and a lot more. One needs to find the form suitable according to his earnings
To be noted: Only form ITR 1, ITR 2 and ITR 4 is available online for individual taxpayers. - Referring to TDS Certificates (Form 16) and Form 26AS – The taxpayer needs to fill the details in his ITR referring to the TDS certificates (Form 16) received annually. Form 26AS is the annual form that helps him to get the sum of the total TDS deducted for the year
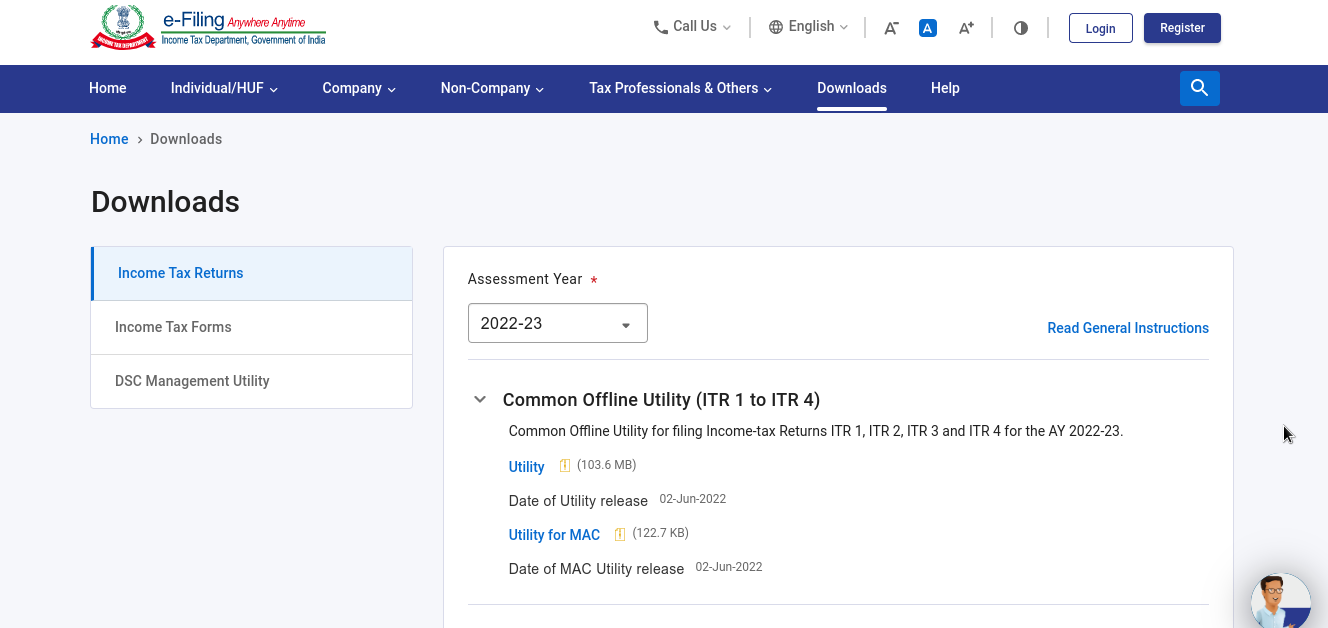
- Income Tax Preparation – Go to the official site for income tax filing (link: www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in) > Go to Downloads then select AY > Download Common Offline Utility> Install the setup
- Fill in the Details – Fill in the appropriate details in the downloaded offline utility. Open the utility then press the ‘File Return’ button> Click on ‘Downloaded Pre-filled Data’ >Enter the PAN and Select the AY > Log-in with your username and password > Enter the accurate information of your income and check the amount payable as tax. One can enter the details of the income-tax challan in the utility
- Verification of the Details – Click on the ‘Validate’ icon visible in the offline utility to re-confirm that all the mandatory grids are filled
- Convert the File into JSON Format – Once the details are validated > select the ‘Download JSON’ button
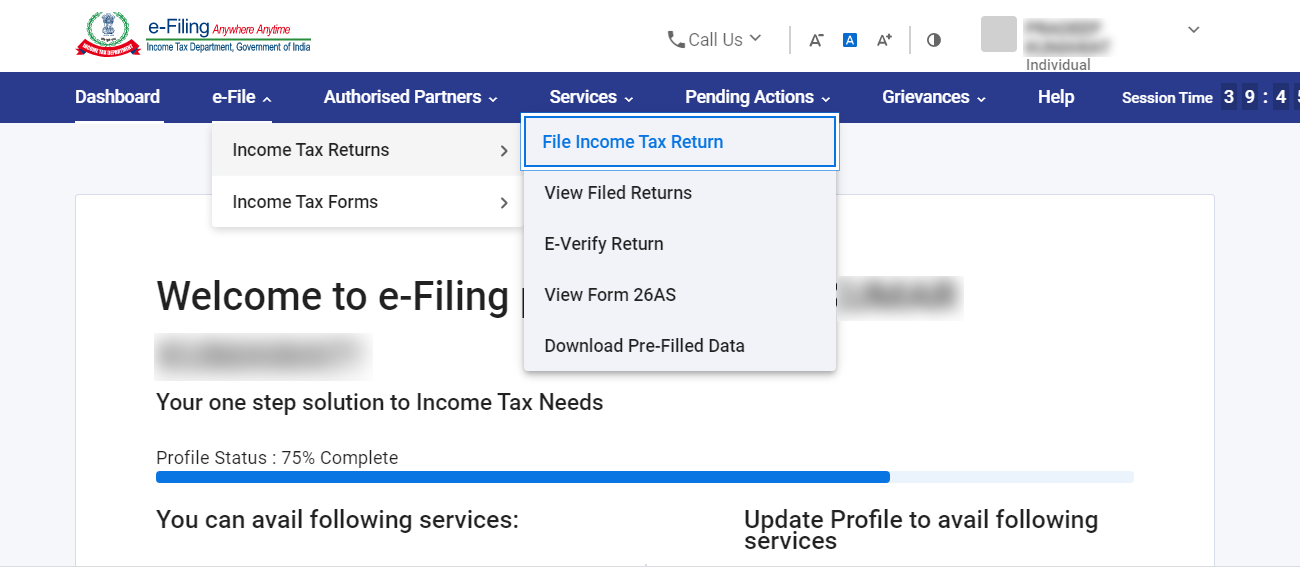
- JSON to IT Portal – The last step is to upload the JSON file on the official income tax portal. Log in to the portal > Select ‘e-file’ > Select ‘Income Tax Return’ option from the dropdown
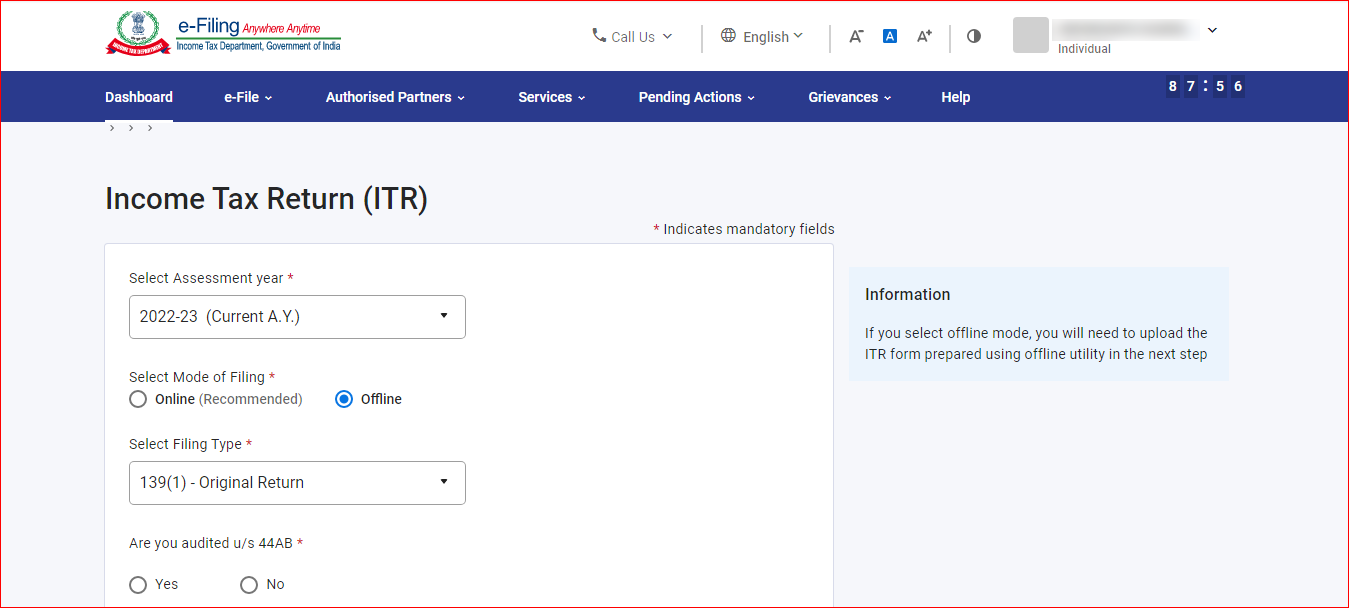
- Fill in the basic identification details like PAN, Assessment Year, ITR Form number and upload the XML File by clicking on the option ‘Upload XML’
- Upload the JSON file on the portal from your computer and finally click on ‘Submit Button’. > select the available verification modes —Aadhaar OTP, electronic verification code (EVC), or sending manually signed copy of ITR-V to CPC, Bengaluru.
Eligibility for Income Tax Return Filing
The eligibility for filing the ITR is decided on the basis of the annual income earned by an individual. Below is the threshold limit that decided to file the returns.
- Individuals below 60 years – Yearly Income Rs.2.5 lakhs or more
- Individuals in between 60 years to 80 years – Yearly Income Rs.3 lakhs or more
- Individuals above 80 years – Yearly Income Rs.5 lakhs or more
There are other factors under which one needs to file the returns like:
- Income Source – Salary, Rent from the property, Income from Business or Profession, etc
- Claiming the refund – It is mandatory by law for an individual to file his ITR if he is claiming a refund from the government.
- Loan or Visa Application – It is easier for an individual to get a loan or visa if he is a constant ITR filer.
- A Business – It is mandatory for every registered company operating in India to file returns.
How to Select ITR Forms for Tax Returns?
| Type of ITR Form | Who can File? | Who can not FIle? |
| ITR 1 (Sahaj) |
|
|
| ITR 2 |
|
|
| ITR 3 |
|
|
| ITR 4 (Suman) |
|
|
| ITR 5 | Any person other than
|
|
| ITR 6 | Companies |
|
| ITR 7 |
|
|
Assessment Year v/s Financial Year
Assessment Year is the period just after the Financial Year. It is the time when the income earned in the preceding Financial Year is computed to judge the tax liability.
Financial Year is the period in which the income is earned by a business, individual or any financial entity. The period is said to start from 1st April to 31 March.
Financial Year 2020-21 is from 1 April 2020 to 31 March 2021 and the period from 1 April 2021 to 31 March 2022 is the Assessment year 2021-22.
Calculating the Payable Income Tax
Make use of the tax calculator to find out the exact amount payable under the tax. The utility is available free of cost online. Using the utility one can find the accurate tax liability for the three consecutive financial years at once. Check Your Payable Income Tax
Deadline for ITR Filing
The due date for filing the income tax returns for Financial Year 2020-21 for non-audit cases is 31st December 2021 while for the audit cases the due date is 15th March 2022 (Revised). One must file the returns on or before the due date in order to avoid penalties.
E-Filing Advised to Non-assessees
Filing a return is always beneficial for the taxpayer as well as the government. Individuals can file a zero return if they are not paying taxes. This is helpful in case of availing of the loan from the bank or applying for a visa.
Multiple Tax Returns file at One Time
Taxpayers can easily file multiple returns from a single account. As effective e-filing Income Tax software helps you file the forms of the current year as well as the previous year under one user account. You can compute the taxable amount and file the returns anywhere and anytime within your comfort zones.
What is Form 16?
The form is meant for salaried employees. Form 16 is given by the employer to the employee from whose salary account TDS is deducted. The form is also known as a TDS certificate. The form is segregated into two parts Form 16A and 16B.
ITR E-filing with Form 16
Below are the steps that will help you with e-filing if you have Form 16:
- Upload Form 16 on the software
- ITR is auto prepared by the software
- Validate the tax details
- Electronically file the ITR and receive the acknowledgement number
- Verify your tax return online through net-banking
Income Tax Return E-filing without Form 16
Below are the steps that will help you with filing returns without form 16 if you do not have:
- Fill in the income details
- Mention the investment under 80C
- The software will help you with the correct form
- Validate the tax details
- Electronically file the returns and receive the acknowledgement number
- Verify your tax return online through net-banking
Tracking ITR-V Status
Once you are done with the entire Income tax e-filing process you will get an intimation from the Income-tax returns -V or Income Tax Return Verification department. The mail containing the ITR-V form will be sent by the tax department on the registered email id of the taxpayer. Download the ITR-V form.
In Case if I lost my Income Tax E-filing Password
There are instances where taxpayers are seen in trouble because they have lost their passwords for Income Tax return filing. One must always store the credential in a safe file the access of which is with the taxpayer himself, concerned CA or accountant.
In such a case there is an option for resetting a password. This can be done by sending a request through an email to the Income Tax Department at validate@incometaxindia.gov.in mentioning the basic details like:
- PAN
- PAN Address
- Name of the PAN holder
- Father’s Name and
- Date of Birth
To be noted: It is suggested to mention the PAN with Aadhaar in the IT Returns. If Aadhaar is not yet received than one can mention the enrollment number in the return.
Frequently Asked Questions About ITR Filing:
Q.1 – Question 1. Who can file the ITR using the offline mode (physical documents)?
Only a certain category of individuals are allowed to file the return in using offline modes like individuals above the age of 80 years at any time during the year and also those whose annual income is less than Rs. 5 lakhs and are not claiming any refund from the government.
Q.2 – How can I mention the Aadhaar Enrollment Number in the ITR?
There is a separate column for mentioning the 28 digits Aadhaar enrollment number in the ITR. First, mention the 14 digits Aadhaar enrollment id then mention the date.
Q.3 – There are deductions that go unnoticed in Form 16. Is it possible to claim the refund on such deductions?
There are various deductions under Sec 80 (ELSS, PPF, Life and health insurance, NSC, Children tuition fees,5 years fixed deposit, donation for charity, repayment of a home loan) that are not mentioned in Form 16 given by the employer. It is possible to claim a refund on such a deduction in the ITR filed by you. You can even claim the HRA in the ITR
Q.4 – What are the consequences of not filing the ITR on or before the due dates?
There is a penalty u/s 234F of Rs. 5,000 if one fails to submit the returns on or before the due dates. However, the amount of penalty shall not go beyond Rs. 1000 if the annual income of the taxpayer is less than or up to Rs. 5 Lacs. However, if the taxpayer has an annual income of more than Rs 5 lacs and he files his return after 31st December then there is a penalty of Rs 10,000 u/s 234F.
Q.5 – Which form do I need to file if my annual income is Rs 50 lacs?
ITR 2 is the annual return form to be filed in case if the taxpayer’s annual income is Rs. 50 lacs or more. He is then not eligible to file ITR 1. The taxpayer also needs to disclose the details of the assets owned by him. Assets and corresponding liabilities are required to be mentioned in Schedule AL of the ITR Form.