Goods and Services Tax is a significant step taken by the government of India to subsume all the additional indirect taxes which was previously levied such as VAT or sales tax, entertainment tax, entry tax, purchase tax, luxury tax, and octroi on the movement and purchase of goods and services. GST is an indirect tax which replaced the multiple cascading effects and is applicable throughout the India. GST council makes rules and regulations for GST and is chaired by Finance Minister of India Mr. Arun Jaitley.
There are five tax slab rates under GST 
Previously, the tax structure was divided into indirect tax and direct tax. GST has resolved the issue of liability transfer to buyers while purchasing the products by the scheme of input tax credit 
GST In India And Other Countries
Now if one acknowledges the working of GST in other nations for understanding the GST implication, first of all, it is a known fact that more than 160 nations have brought up GST and as a matter of fact, European tax economy has conceived the GST more than 50 years ago.
In the Asia Pacific geography, the taxation scheme is a popular and broadly accepted subject of taxation. But the most important and questionable thought over this discussion concludes that there are above 40 models of GST applications which are currently running through the system of various economies in the world which includes a diverse set of rules and regulations.
Let’s have a look on the greater economies and their GST implementation:
GST India vs GST New Zealand
GST has been implemented in New Zealand in 1986 and after that, it had been applying the taxes on everything at a single and consistent rate which is 10% till 2010. The tax rate after 2010 has increased to 15% which is applicable to all purchases. There is no GST on residential rents and financial services. Here businesses can also recover the GST as an input cost.
GST India vs GST Singapore
Singapore also follows the single and consistent rate system on every purchase. GST was initiated in Singapore in 1994 with the flat GST rate of 3% which was lowest in the market. With effect from 2007, the GST rate has been increased to 7% which is still very less compared to GST rates of India.
GST India vs GST Indonesia
In Indonesia, imports are subject to VAT and GST, but most of the exports are exempted from the list of it. The tax rate is 10% if the services are supplied out of Indonesia by foreign taxpayers, and certain items are taxed at 20% with the cap of 35%. The luxury tax which is applicable on import is 10% to 50%. Most of the items like gold, mining products, arts and entertainment, education, insurance, parking, public transport, medical health, labour, hotel, financial, food and beverage served in hotels are not subject to pay any VAT.
GST India vs GST China
After the European and Asia Pacific market, the China has maintained the GST applications over goods and the conditioned provision of repairs, processing and replacement assisted services, which also means that it is restrictedly collected on goods which are consumed in the manufacturing process as the fixed asset goods and service tax in foreign country like China is not under recoverable terms. There are three tax rates; which includes 0%, 5%, and 19%.
GST India vs GST Australia
Going to the far shores, in Australia, the GST is a federal tax which is collected by the supreme authority and thus divided further among the states without any conflict arising through the process. The GST was firstly introduced in 2000 with the tax rate of 10% which is consistent till date.
GST India vs GST Canada
Now looking to Canada model of GST, the country governs the taxation regime under 3 schemes i.e. Federal GST, Joint federal and separate federal. Federal tax is generally accepted tax system while joint federal runs on the basis of the synchronized behavior of the economy and states and the last one separate federal which only applies to the Quebec as it is deemed as a quasi-independent province. The GST rate in Canada is 5% on supplies of goods and services and in some provinces, there is harmonised sales tax which is 15%.
GST India vs GST Brazil
Talking about the Brazil model of GST, it is much independent and carefree in comparison to other nations and has a dividing rule of taxes between the states and the center. Brazil has six tax slabs which are 0%, 1.65%, 2%, 7%, 12%, and 17%.
GST India vs GST USA
The US is a federal republic where taxes are collected at a separate level from federal, state, and local governments. Here the federal tax rates are between 10% and 39.6% of taxable income while state and local government is charging the tax from 0% to 13.30% of total taxable income.
GST India vs GST UK
In the UK there are three tax rates including 0%, 5%, and 20% applicable on goods and services. Most of the goods are covered under 20% tax rates. The VAT on postage stamps, financial, property transactions, most food and children’s clothes are exempt from any tax.
GST India vs GST France
GST has been firstly implemented in France in 1954 with 4 tax rate slabs. The rates here are chargeable in the slab of 2.1%, 5.5%, 10% and 20%. Among the tax rates, 20% is the standard rate applicable to most of the goods in France.
GST India vs GST Ukraine
In Ukraine, there is a standard tax rate which is 20% and the VAT value is added to the cost of Goods and service price. There are some of the supplies are also subject to lower rates under 0% and 7%. Generally, 7% rate is applicable to pharmaceutical products, medicines and medical equipment while the export of goods and services attract 0% VAT.
GST India vs GST Malaysia
GST has been implemented in Malaysia with effect from 1 April 2015 with the consistent rate of 6%. Here, Sales tax and service tax are categorised by different tax rates which are 10% and 6% respectively. Some of the items like piped water, first 200 units of electricity per month, transportation services, highway toll and health service are exempted from taxation.
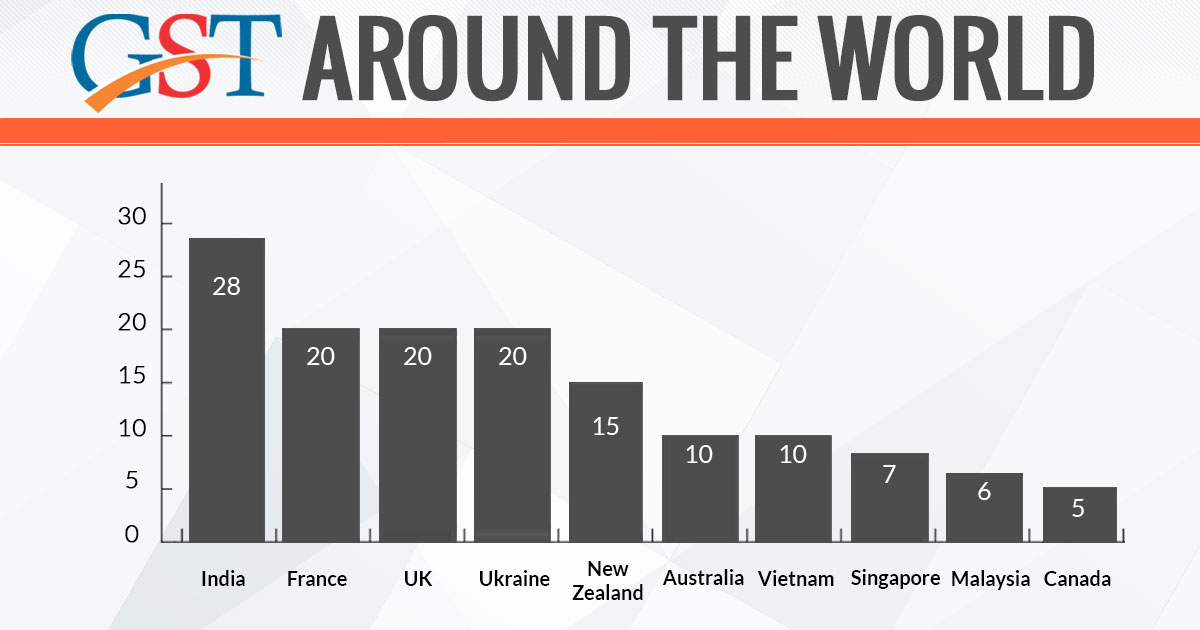
In all cases, GST rates are prefixed between 16 to 20 percent and India has somehow taken the cues from this and jotted down the similar pattern. Also, it is expected that the Indian economy will expand with a great pace as the speculated taxpaying community is likely to get a growth of 5 to 6 times than the current figure.










Jab humare desh mein GST mmf pe dusre country se jayada hogi to humaara desh kaise comption mein maal sale/export karega.
Jab humare desh mein million log is mmf mein se roji roti kamaao ke kha rahe hai.