
The major purpose of incorporating GST was to digitise tax compliance to make the process simpler and attain an effective rise in the collection of tax. With the execution of GST in July 2017, it would have delivered better developments.
Similar to thinking over real-time reporting and e-invoicing, let’s see the issues that the tax administration has faced, and the difference between the expected GST revenue and the actual amount collected.
Tax evasion, incorrect reporting, and administrative errors can be the cause of the above-stated gap. Various measures, such as the notice on the difference in the reported information towards returns and e-way bill relevant checks in the transportation and others would have been chosen to resolve the leakage.
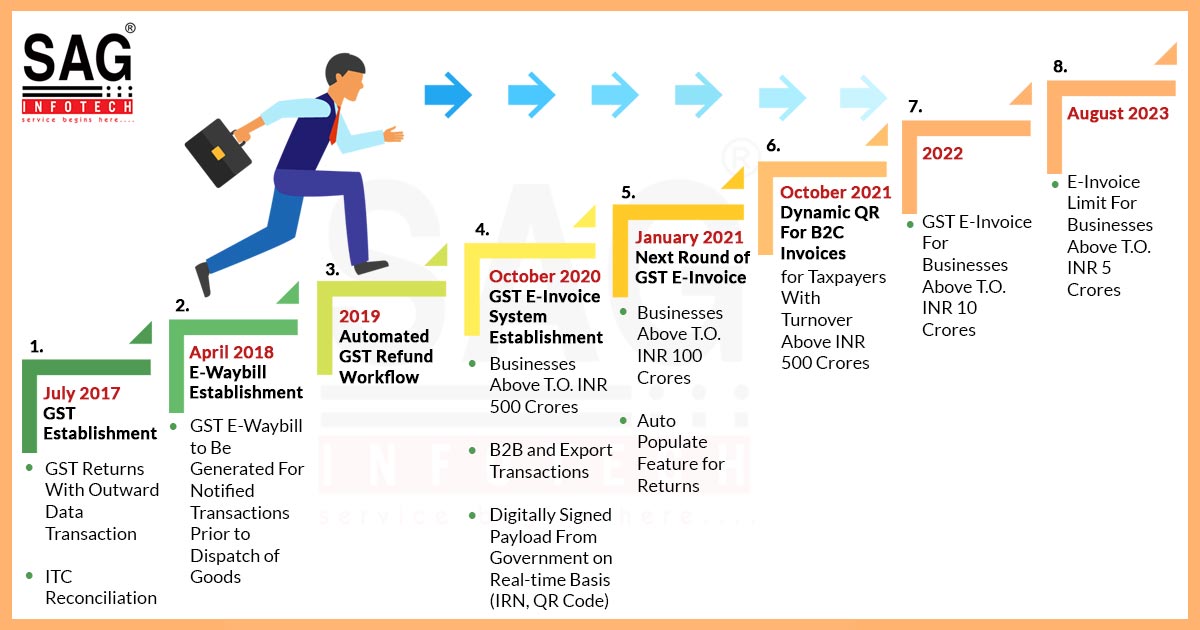
E-invoices were introduced on 01 October 2020 because it was not good to fetch and remove the tax evasion and make the practices effective through chasing paper trails. Moreover, a central de-duplication utility has been initiated to make sure that no identical transaction reported twice. For singular reporting of common data, a link with the GST e-Way bill system would be required.
In the year 2020, much more adaptability would be revealed in the business during the start of the pandemic, along with the execution of the electronic invoice regime in India made by the government and companies. Through the arrival of e-invoicing, inter-operability between two government portals, the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) made for the validation and signing of the e-invoicing and GST return portal, for transaction reporting and GST return filing was tested.
Read Also: Best GST Return e-Filing & Billing Software for CA Business
The effective blend of e-invoicing with real-time reporting has also rationalised the exchange of invoice data between multiple businesses.
Through the phased launch of e-invoice (applicable dated 1st April 2022 for businesses with a yearly turnover limit of US$27,000 or INR 200 million), the same would be an essential rise in the real-time reporting and monitoring of the GST collections.
In June 2022, the government would have assigned 5 additional invoice registration portals (IRPs) with the objective of furnishing an easier GST e-invoice generation experience for assessees.
Exchanging Tax Details Between Authorities
Mentioned that in the multi-registration environment where businesses function in the present, digital tax administration (DTA) would have taken on higher importance. The information for the GST is much more the tax administrators would be leveraging a centralised system to ease the exchange among states for the effective administration of the interstate trade and consistency of the taxes.
For the registration, return filing and e-payment, the revolutionary goods and services tax network (GSTN), GST’s IT infrastructure, furnishes a common platform for the e-invoices would get generated via authorised invoice registration portal (IRPs). GSTN used to furnish a shared IT platform to all the GST stakeholders and combines the tax administration systems of the centre as well as the states.
Fast Strides in Digital Tax Administration (DTA)
To make the systems and processes effective and efficient, the government is continuously investing and would direct towards the development of the framework in which the data triangulation would be enabled. For instance, the income tax along with the GST databases would now be integrated, that permitting the comparison of the transactions notified on either platform.
The information recorded in Form 26AS would compare with the GSTR-1 filings. With FASTag data e-way, bill filings are triangulated. Making Aadhaar authentication mandatory shall furnish a single reference within numerous databases of the government. Through the ITC, specifically in duration, data sharing with the purchaser would become real-time.
For the case of the vendor who does not deposit the taxes or the transaction is not mentioned by the vendor, the provision for the ability to recover from the purchaser would be made, and the need for the whole chain to be compliant on a near-real-time basis. The same would revise the complete compliance quality. It seems that the expansion of e-invoice needs will continue. On the side of analytics, the government would develop the traceability of transactions via various supply chains by developing network visualisation all over the country.
Proper Communication in the GST E-invoice System
Through the direction from the additional jurisdictions and the Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement On-Line) network, the discussions would be towards establishing a peer-to-peer communication network in which the signed e-invoices could be communicated to the opposite party.
Below would be the variants needed to be acknowledged:
- The customer received the confirmation via the tax authority on the signed e-invoice.
- Decentralised clearance would be available, in which the communication is between multiple enrolled invoice service providers.
- The customer determines and notifies errors or mismatches on the e-invoice by requesting the credit not to amend the errors.
- The acceptance of the e-invoice would be recorded by the customer prior to the same becoming a valid tax invoice.
With the use of e-invoices, the communication of the transaction-level information shall become quicker and more detailed. The same would make the accounts payable processes automatic, and the same will remove the manual steps that the assessee is currently used to performing. The trade might leverage optional data in the policy to convey more detailed data to the opposition.
Mera Bill Mera Adhikar Scheme for B2C Invoices
The government is doing an operation to draw the invoice incentivization or the Mera Bill Mera Adhikar scheme to incentivise citizens and consumers to seek the genuine invoice from the sellers (particularly to those who cater predominantly to the B2C market). As per the proposal, B2C invoices (when the buyer opts) would get notified on the designated government portal to choose a reference number on a real-time basis. The reference number might act like a lottery number to the purchaser, in which the winner would be rewarded on the grounds of a raffle at the end of the duration. The major goal is to rectify the compliance quality.
Assessee to be Actioned
For the assessee, what do several developments in the GST mean? To learn the same, we are required to know the major facts of the company that would be influenced by some of these developments.
- Technology Tax
- Dealing with DTA
- Management Data
- Talent needs to deal with the amendment in conditions.
- Matching the growing business with tax, along with technology dynamics.
- Reputational risk and the financial loss risk on the basis of interest and penalty in case of process failures.
The 3 above-mentioned 6 points are relevant to technology, big data, and dealing with the tax administration.
The major thing would be to set the effective systems and the processes towards:
- Analytics
- Record-keeping
- Reconciliations
- Engagement with Regulators
- Exception Management









