What is the Full Form of GST?
Generally, GST refers to the Goods and Services Tax. To replace several indirect taxes prevalent earlier in India, a new type of tax was introduced. Most indirect taxes, excluding some state taxes, are included in GST, a multistage, destination-based tax.
Here, we are explaining all the related aspects of taxation and GST.
All Types of GST
The three main components of taxation are CGST, SGST, and IGST. A brief introduction for the beginners, as to exactly what all these components mean and what role they play in the taxation economy of the GST.
Goods and service tax comprise CGST, SGST, and IGST. CGST and IGST are levied by the Central Government and SGST is levied by the State Government.
GST the goods and service tax is a reformative financial taxation scheme introduced in the Indian constitution for structuring all the business units into the database of tax-paying organizations with equal consideration.
The goods and service tax is implemented to subsume all the indirect taxes.
Get Free Demo of GST Filing & Billing Software
The Meaning of CGST with Full Form
CGST means Central Goods and Service Tax. CGST is a part of the goods and service tax. It is covered under the Central Goods and Service Tax Act, of 2017.
Taxes collected under the Central Goods and Services Tax will be the revenue for the central Government. Old Central taxes like Central excise duty, Additional Excise duty, Special Excise Duty, Central Sales Tax, Service Tax etc. have been subsumed under Central Goods And Service Tax.
The Meaning of SGST with Full Form
SGST means State Goods and Service Tax. It is covered under the State Goods and Service Tax Act 2017. A collection of SGST will be the revenue for the State Government. All the state taxes like Value Added Tax, Entertainment Tax, Luxury Tax, Entry Tax etc. have been merged under SGST. For example, if goods are sold or services are provided within the State then SGST will be levied on such transaction.
Read Also: Latest GST Notifications on Tax and Rate
The Meaning of IGST with Full Form
IGST means Integrated Goods and Service Tax. IGST falls under the Integrated Goods and Service Tax Act 2017. Revenue collected from IGST is divided between the Central Government and the State Government as per the rates specified by the government. IGST is to charge when the transfer of goods and services from one state to another state.
Import of Goods and Services is to be covered under Inter-state transactions so IGST is to be levied on such transactions. For example, if Goods or services are transferred from Rajasthan to Maharashtra then the transaction attracts IGST.
Threshold Limit to Pay GST In Case of Intra-state or Inter-State Trade
In the case of intra-state supplies, the limit for all dealers exceeding a turnover of Rs. 20 lakhs and above except the North Eastern States where the limit is Rs. 10 lakhs and above. The dealers registered under the composition scheme can avail of the benefits within the state only if their turnover is under Rs. 1.5 crore.
A taxpayer whose annual turnover is less than or below INR 1 crore in a financial year, turnover for special category States, i.e. Jammu & Kashmir and Uttarakhand, while for the northeastern states, the limit is up to Rs 75 Lakhs.
In the case of inter-state supplies, GST is applicable to all kinds of supplies. It does not involve the turnover factor in the inter-state trade. But as per Notification No. 10/2017 Integrated Tax dated 13th October 2017, Govt. has exempted from obtaining registration for the persons making inter-state supplies of taxable services and having an aggregate turnover not exceeding an amount of Rs. 20 lakhs in a financial year.
A Proper Explanation of Adjustment of Input Tax Credit under CGST/SGST/IGST
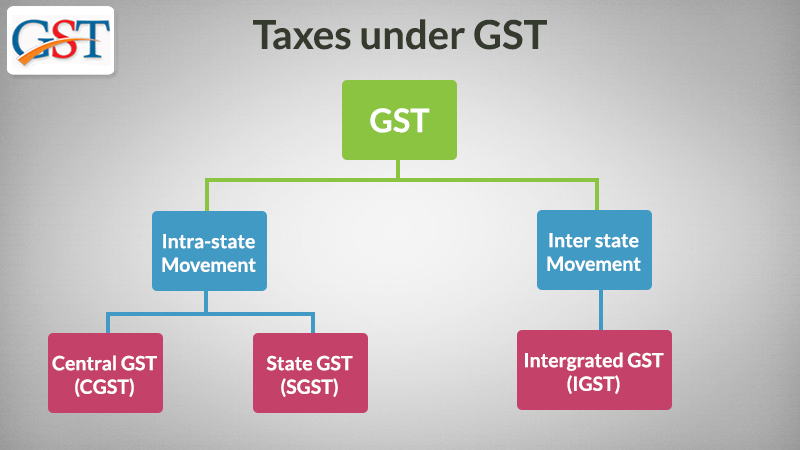
As known, the Goods and Services Tax is a destination-based tax that would be applicable at the place of the consumption of goods or services. State GST, Central GST and integrated GST are levied on the account of one tax regime across the nation.
Central GST is levied by the central government on every intra-state supply of goods and services and the same fact is applicable to the State GST. For the inter-state supply of goods and services and for the imports, there is Integrated GST applicable which will be collected by the centre.
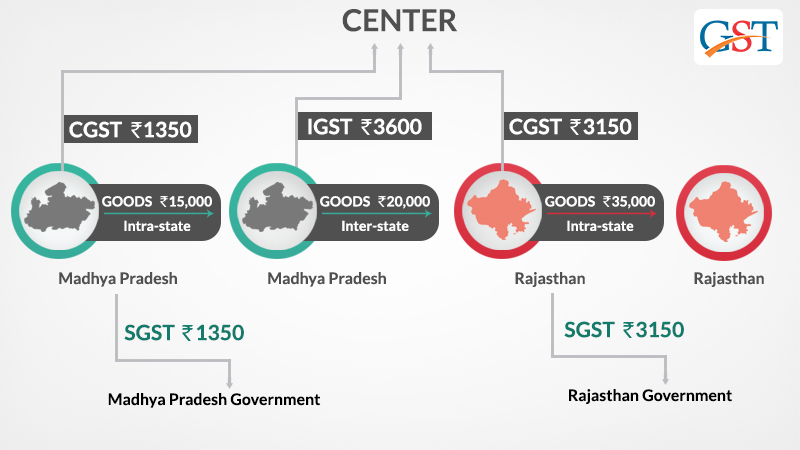
For the understanding purpose, if a dealer in Madhya Pradesh sold goods to a consumer in Madhya Pradesh worth Rs. 15,000. The GST rate is 18% comprising of a CGST rate of 9% and SGST rate of 9%, in such case the dealer collects Rs. 2700 and Rs. 1350 will go to the central government and Rs. 1350 will go to the Madhya Pradesh government.
Read Also: Brief Guide of Reverse Charge Mechanism Under GST India
How ITC will be Calculated by the States and the Centre?
Suppose goods worth Rs.15000 are sold by manufacturer A in Madhya Pradesh to Dealer B in Madhya Pradesh. B resells them to trader C in Rajasthan for Rs. 20000. Trader C finally sells to End User D in Rajasthan for Rs. 35,000.
Suppose CGST= 9%, SGST=9%. Therefore, IGST=9+9=18%. Since A is selling this to B in Madhya Pradesh itself, it is an intra-state sale and both CGST @9% and SGST@9% will apply. B (Madhya Pradesh) is selling to C (Rajasthan). Since it is an interstate sale, IGST @18 % will apply. C (Rajasthan) is selling to D also in Rajasthan. Once again it is an intra-state sale and both CGST @9% and SGST@9% will apply.
The condition is that Any IGST credit will first be applied to set off IGST then CGST. The balance will be applied to set off SGST.
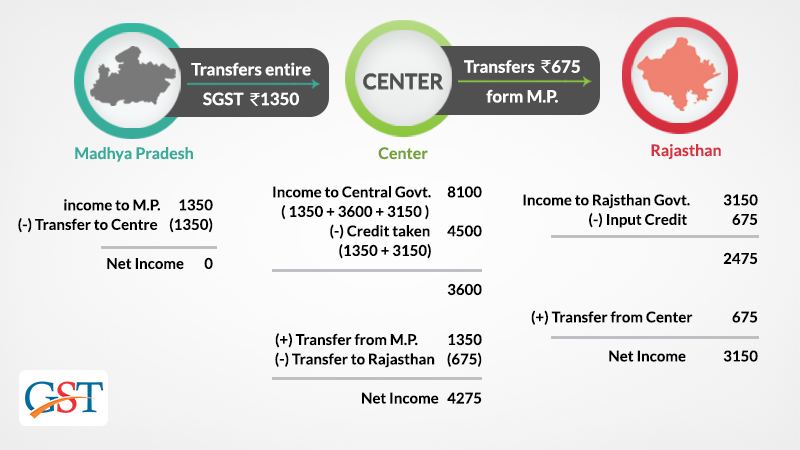
The taxpayers’ work is done till step III. But as GST is a consumption-based tax, i.e., the state where the goods were consumed will collect GST. So, Madhya Pradesh (where goods were sold) must not get any taxes. Rajasthan and Central both must have got (35,000*9%) = 3150 each. Madhya Pradesh (exporting state) will transfer to the Centre the credit of SGST of Rs. 1350 used in payment of IGST. The Centre will transfer to Rajasthan (importing state) Rs. 675 IGST credit used.
Normal GST Implementation
Union finance minister stated that the GST i.e. Goods and services tax is a simple tax mechanism for the traders who want to expand the portfolio of business across the nation.
Interest on Late Payment of GST Tax and Penalty on Missing GST Due Date
According to the GST council rules and regulations, each subsequent will accrue 18 per cent per annum interest on the GST tax payable starting from the due date till the payment date of taxes. You can read detailed interest guides in chapter 10, point 50 here: https://cbic-gst.gov.in/aces/Documents/CGST-bill-e.pdf
For Example: If a taxpayer misses the deadline for GST tax payment then there will be interest calculations commencing from the due date i.e. 1000*18/100*1/365= Rs. 0.49 per day approx.
(Rs. 1000 is the assumed tax payment) (18% per annum is the interest rate) (1 day delayed by the taxpayer)
In case if a taxpayer does not file his/her return within the due dates mentioned above, he shall have to pay a late fee of Rs. 50/day i.e. Rs. 25 per day in each CGST and SGST (in case of any tax liability) and Rs. 20/day i.e. Rs. 10/- day in each CGST and SGST (in case of Nil tax liability) subject to a maximum of Rs. 5000/-, from the due date to the date when the returns are actually filed.
What are the Concerning Points of the CGST, SGST or IGST applicable?
It is important to see through some of the points when taxation is applicable on transactions whether it is Central Goods & Services Tax (CGST), State Goods & Services Tax (SGST) or Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST) which will further watch out the Intra State or an Inter-State supply.
When the location is the same state for both supplier and the place of supply i.e., the location of the buyer that is considered as an Intra-State supply of goods or services. In the same state, the seller is made to collect both CGST and SGST from the buyer in the Intra-State transactions.
The Inter-State supply of goods or services is considered when the location of the supplier and the place of supply are done in different states. When the SEZ unit is to have the export or import of goods or services and supply of goods or services is made to or by and the transactions are still Inter-State. While the seller needs to collect IGST from the buyer in the Inter-State transaction.









Our gstr 9 &9c filed but dr. Note show & cr. Note not show and any return
Annual return once Filed can not be rectified, if there is any liability arise on your end then kindly pay the same via DRC-03
hello sir
meri igst me sale jayda h but input credit mera sgst me pada huaa to kyaa hum igst ko sgst se pay kr skate
Yes provided SGST liability should be the first set off, then after that, you can set off the ISGT liability with SGST ITC credit
Can u please explain how the input credit for Rajasthan (675) is calculated above.
Please explain the above question
सर रेलवे रसीद बनाते समय gst नम्बर डालना भूल गया gst का पैसा igst मे ना जाकर cgst /sgst मे चला गया इसका रिफंड का कोई प्रावधान है क्या
No
Respected Madam/Sir,
If any mandatory Collection Example GST Number Pan for the Inter-State Sales
Please specify the Question correctly
Hello sir/mam.
Kya aap bta skte h ki sgst or cgst dono customer ko pay krne hote h. Mne ek laptop liya rohtak se to mje sgst or cgst dono pay krne pade . plz answer me.
I IGST Input credit available will it adjust with CGST and SGST
Yes, it can be adjusted with CGST & SGST
Hello, I am a cashier how to return the GST bills
sir, I am in a accounts assistant. I have received other state purchase bill so which taxes applicable in this bill. Please explain clearly.
Since the purchase is interstate, IGST is applicable. It depends upon your “place of supply” whether the transaction is intrastate or interstate and accordingly taxes are applicable.
Hi, I am Mukkerla Saidulu. I am a chartered accountant. I have done my (B.Com) from Suryapet Kakatiya University. I have a keen interest in the taxation field.
Read here: https://blog.saginfotech.com/register-for-gst-practitioner
Very well explained…
Hi,
I’m Veeraraghavan, doing cosmetics product dealership in Tamil Nadu only. We have old stock before GST around 4 lakes VAT is 14.5%.
However if we sale these old products now, for GST filing CGST 9% only will adjust from old ITC and I need to pay balance SGST 9%. Where we claim this amount? from my product manufacture or GST?
Example : last month we sold products Rs.100000.00 , GST is 18% = 18000.00. If filing GST only CGST will adjust old ITC balance, however, I need to pay SGST 9% to the government.
So, where can I claim this 9% SGST?
if the materials are delivered at Gurugram, but party belong to thane how can do e waybill?
Hi,
I have IGST input 118933 and CGST 11441 and SGST 11441. Output IGST 0 and CGST 74444 and SGST 74444. How will adjust the IGST input for SGST and CGST?
You first need to setoff liability from CGST credit and then only you can utilize the ITC of IGST and SGST.
Sir, IGST, CGST, SGST Hindi me details likh do
Read Here: https://translate.googleusercontent.com/translate_c?depth=1&rurl=translate.google.com&sl=auto&sp=nmt4&tl=hi&u=https://blog.saginfotech.com/meaning-of-sgst-igst-cgst&xid=17259,15700021,15700186,15700190,15700256,15700259,15700262,15700265,15700271&usg=ALkJrhibGpcxY7RkaR6TwenGhBEAYhDZ5A
IAM sending goods from Belgaum to Pondicherry which GST will be applicable
CGST, SGST , UGST, OR IGST
IGST
IGST INPUT 118933 CGST INPUT 11441 – SGST INPUT 11441 –
CGST OUTPUT 74444 SGST OUTPUT 74444
————– —————
63003 63003
————- ——————–
ADJUSTMENT IGST INPUT 118933 –
CGST AMT 63003
—————-
55930 –
SGST AMT 63003
————–
SGST PAYABLE 7073
===========
GST charged on freight bill by GTA @ 5% or 12%. GST input credit available or not for the recipient?
In case of GTA, tax to be paid is 5% without ITC or 12 % with ITC and ITC of the tax paid for GTA will be available.
Available credit in CGST in union territory can it be used for payment of other state GST for the same company with different registration numbers.
yes
nice infromation
V are being educated to help out our families come up better …. But even that education is a burden for children specially in tamilnadu
I am imposed with heavy tax including cgst and sgst even in student Xerox… Shops in tamil nadu… Then even our assignments and even a single paper are rated high….
I belong to a low class family.. I study by loan of around 4 and half lakhs including both degree and post graduation course In nursing… How can me and my family survive meeting all these heavy cost and my father is handicapped and is a farmer….
WE THE CONTRACTORS HAVE 3-6 MONTHS OLD CIVIL WORKS BILL PENDING AT PUBLIC WORKS DEPARTMENT. TILL DATE BILL NOT SANCTIONED. NOW IT IS TO BE SANCTIONED DURING THIS MONTH. CAN WE PAID GST NOW. THEN WHAT WE CAN DO IN THIS CASE
for home stays (lodges) if GST is registered and total turn over is less than 20 lacs per annum, does the paid GST is back credited or not. OR if registered under GST and even turn over is below 20lacs need to PAT GST and not credited back.
Hi,
I am K Singh if I have got GSTIN and New work in service sectors but still, don’t have any project. So should I inform to anywhere that my business still is in wait mean no revenue?
BR,
K Singh
Dear Sir,
I want information about IGST Refund claim Example:we import good from other country and pay IGST 18%
and sale in domestic so we can take refund 18% or not if we paid 18% Rs 15000/- and when we sale same instruments in india including our margin and collect IGST from Customer 16000/- so need to goverment 1000
correct then after we can take 18% IGST which was we paid at the time import .
Exact information about CGST, SGST and IGST
very good knowledge, of IGST, CGST, SGST. please update once new rules will come.
Kindly regards
Manoj Savtadkar
SCM.
Hi,I am PRAMOD SONWANE. I have done my (M.Com) from Aurangabad University. I have keen interest in taxation field. IGST CGST & IGST Adjustment.
HOW I M UPDATE ALL HSN NO. IN ALL MEDICINE ITEM
I M FARMACY ASSISTANT
HAI I AM CHEMIST HOW I CAN ADJUSTMENT OF STOCK BEFORE GST
Hi,I am Lalit Sarswat. I am an account executive. I have done my (B.Com) from mgsu.university. I have keen interest in taxation field. IGST CGST & IGST Adjustment.
IF WE HAVE 13 MONTH OLD STOCK (RAW MATERIEL) BUT EXCISE MODVAT ALREADY USED THEN WHAT I CAN DO IN THIS CASE
no credit will be allowed now
Hi,I am omprakash yadav . I am a account executive. I have done my (B.Com) from m.d.university. I have keen interest in taxation field. IGST CGST & IGST Adjustment.
thank you for knowledge me(am ca student)
thank u all
Kindly highlight on the interstate travels ,octroi and permit for interstate travel
Any changes prosposed in value of permit fees.
i have only one place of business and not having business verticals in particular state then GSTIN Numbers are separate for SGCT, CGST and IGST Act or there is only one GSTIN for all that act in a particular state.
Only one GSTN for SGST, CGST & IGST.
yes
there is one gstin for business in single state and if u do business in other state also then u take second registration also which is mandatory
One state GST will not be applied to another state. If you want to do business in another state then you have to surrender old GST and apply new GST.