
What is GSTR 9C (GST Audit Form)?
GSTR 9C is an annual audit form for all taxpayers having the turnover above 5 crores in a particular financial year. Along with the GSTR 9C audit form, the taxpayer will also have to fill up the reconciliation statement along with the certification of an audit.
- Latest Updates of GSTR 9C Form
- GST Audit Types with Auditable Documents
- Who is Required to File GSTR 9C
- Significance of GSTR 9C Audit Form
- How to File the GSTR 9C Form?
- General Queries on GSTR 9C Form
- GSTR 9C Filing By Gen GST Software
Latest News/Updates of GSTR 9C Form
- “The consolidated FAQs for GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C are now available on the GSTN portal.” Read PDF
- ICAI Introduces a Revised Technical Guide on GSTR-9C in Line with the GST 2.0 Framework. read pdf
- The GST Network (GSTN) has provided helpful answers to common questions about different sections of GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C. Read FAQs
- Latest Changes of GSTR 9C For FY 2024-25
- New field (7D1) added in Table 7
- Computation logic modified for Table 7E
- New field (K-2) added in Table 9
- Label changes made for Table 9Q
- Label changed for Table 11 heading
- New field (G2) added in Table 11
- Label changes made for Part V heading
- GSTN Notification No. 15/2025 relates to the exemption of GSTR-9C taxpayers with a turnover of up to INR 2 crores. View more
- The latest GSTR-9C circular clarifies the applicability of late fees for delayed form submissions. Read PDF
SAG Infotech is here to provide all the relevant details of the GSTR 9 and 9C forms and a step-by-step procedure to file them along with the screenshots. The GSTR 9C form has a reconciliation statement for reconciling turnover, input tax credits and tax payments. The taxpayers can also view and download the GSTR 9C form in PDF format.
GST Burden Reduced for FY 2024-25
| Sales | GSTR 9 | GSTR 9C |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 2 Cr | Exempt (From FY 2024-25 onwards) Read Notification | N/A |
| More than 2Cr. – 5 Cr | Filling is mandatory | Optional (Benefit Given) |
| More than 5Cr | Filling is mandatory | Filling is mandatory |
File GSTR 9C Audit Form Via Gen GST Software, Get Demo!
Simplify GSTR 9C Filing by CBIC
Some exemptions have been done in this form listed below:
- Part of the turnover adjustments necessary in Table 5B to 5N is now not mandatory and all the adjustments now necessary to be described in Table 5O;
- Tables 12B, 12C and 14 (ITC reconciliation) are now not mandatory;
- A few changes are done in the Declaration part also.
GST Audit Types with Auditable Accounts and Documents
The audit beneath the GST consists of the investigation of the records, returns, and audit for all the additional documents that are maintained through the enrolled individual beneath GST. The audit checks the correctness of the mentioned turnover, taxes which are furnished if the refund is availed and if there is any ITC claimed and validates the additional things that are essentially required to get investigated through the expert authority.
How Many Types of GST Audits are There?
Turnover-Based GST Audit: CA or the cost accountant used to implement it and the CA is arranged by the assessee they shall execute the audit if the turnover of the assessee is more than Rs 5 cr under the CGST act, then he shall need to get his accounts audited through the same people.
Normal Audit Under GST: It gets executed through the commissioner of the CGST/SGST or any Officer who has been permitted by the commissioner. The audit in these types of cases will get executed by giving 15 days’ notice before the commissioner.
Special GST Audit: The audit beneath this shall be taken by the CA or the cost accountant who gets appointed through the commissioner. To execute the audit the professional needs to get the order of the Deputy or Assistant Commissioner and indeed the permission of the commissioner.
Qualification of Auditor
Only the CA or the cost accountant can take out the GST audit beneath section 35 of the GST act.
Important Note:
- An internal auditor shall not bring out the GST Audit
- Any individual who uses GST shall not be a GST auditor under the GST Act
- The GST power is provided to the CA or Cost Accountant or they are an employee of any firm of Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant
- The CA or Cost Accountant must not be enrolled under the GST practitioner if they are provided with the audit report
GST Auditor Appointment
GST auditor will be appointed at the start of the fiscal year and towards the company, a GST auditor will be appointed through the proprietor or any partner or the board of directors could appoint them.
GST Auditor Review the Following Accounts
There are various accounts that must be reviewed by the GST auditor
- Register of Stocks
- Ledger of expenses
- Register of Purchases
- Register of Sale
- If there’s any Input Tax Credit that is claimed or practised
- Output Tax which is payable and if paid
- When under the guidelines of the act and there was an e-way bill that was generated
- E-invoice and if IRN is generated and is has a record
- additional accounts which are communicated by the GST Department for the financial year.
Credentials Needed to be Filed through the Assessee
The assessee needs the mentioned documents:
- PAN-based Audited Financial Statements
- Yearly return mentioned in Form GSTR-9 and it must be for every GSTIN.
- Form GSTR-9C which consists of a certified reconciliation statement and it shows the reconciled value of supplies and declaration of tax amounts in Form GSTR-9 that will be compared to audited financials in part A and this must consist of Part B which will be the audit report.
What is GSTR 9C Annual GST Audit Form?
As per the rules, all the taxpayers will have to file an annual return form with GSTR 9 but now in an addition to the current rule, Section 35 of CGST Act, 2017, all those taxpayers having turnover exceeding 2 crores in a financial year will have to submit audited annual accounts along with a reconciliation statement in GSTR 9C form.
Who is Required to File the GSTR 9C (GST Audit Form)?
All those taxpayers having a turnover above 2 crores in a financial year are required to file GSTR 9C form along with the reconciliation statement and certification of an audit.
Due Date for Filing GSTR 9C Audit Form Under GST
The Indian government has disclosed the due date of the GSTR 9C (Reconciliation Statement) form for the FY 2025-26:
- Financial Year 2025-26 – 31st December 2026
- Financial Year 2024-25 – 31st December 2025
Note: “Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) notified the amendments regarding the simplification of GSTR-9 (Annual Return) and GSTR-9C (Reconciliation Statement) which inter-alia allow the taxpayers to not to provide split of input tax credit availed on inputs, input services and capital goods and to not to provide HSN level information of outputs or inputs, etc. for the financial year 2017-18 and 2018-19.”
GSTR 9C Audit Form Penalty Norms If Miss the Last Date
- As per the penalty provisions of the GSTR 9C audit return form, the registered taxpayer has to pay Rs. 200 per day as a penalty of which Rs. 100 consists of SGST and Rs. 100 for CGST. Also, it is to be noted that the total penalty cannot exceed 0.50% of the total turnover on which the said the penalty is being levied.
- Taxpayers with a turnover up to Rs. 5 crores will have to pay SGST and CGST of Rs.50 per day as a penalty from the financial year 2022-23 onwards. In the case of turnover exceeding Rs.5 crore, the late fee would be Rs.100, which includes Rs. 50 for SGST and Rs.50 for CGST. read more
Where to Download GSTR 9C Offline Utility?
The government has released the file an annual return form with GSTR 9C which can be filed up by the taxpayers and then uploaded to the portal. The offline utility is given in a zip folder which has to be downloaded:
- To download the offline utility for the GSTR 9C first visit the gst.gov.in portal
- Opt on the download tab on the main menu
- Now click on the offline tools in the option and it will redirect to the download page
- Click on the download option and extract the file
Where to Find GSTR 9C Online Filing Option on Portal?
Also, there is now an available GSTR 9C online utility. To start filing the GSTR 9C reconciliation audit report, perform the given steps:
- First of all, login with username id & password on www.gst.gov.in
- After that, the dashboard will open, click on the ‘Annual Return’ tab
- Now click on the financial year for the desired period to file the return, click on the FY 2017-18
- An option like ‘Initiate E-filing will appear on the screen, click on that
- But as soon as you will select the filing option, you will be asked for filing GSTR 9 form before you can file reconciliation form. Know more
Items Included While Calculating Turnover for GST Audit:
- All taxable supplies, including intra-state and inter-state apart from the ones which attract a reverse charge, will be included.
- Supplies involved between two business verticals
- Goods or supplies that are sent/received by the job worker on principal to principal basis.
- All export/zero-rated supplies
- Supplies made by agent/job work on behalf of the principal
- All exempt supplies
- All taxes apart from the ones covered under GST. For example entertainment tax paid against the sale of tickets
Items Excluded While Calculating Turnover for GST Audit:
- All inward supplies against which tax is paid under reverse charge.
- All kinds of taxes and cess part of Goods and Service Tax like SGST, CGST or IGST, etc.
- Goods that are received back or supplied to a Job Worker
- Activities that are not part of goods or services under schedule III of the CGST Act
How to File the GST Audit Form GSTR 9C – Step by Step:
- The GSTR-9C has two major parts:
GSTR 9C Part-A: Reconciliation Statement Format
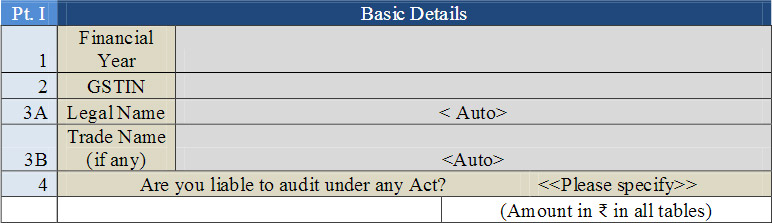
Part 1: Basic Details has the following four sections: Financial Year for which return is being filed.
- 1. Financial Year
- 2. GSTIN of the taxpayer
- 3A. Legal Name of the registered person
- 3B. Trade Name (if any) of the registered business
- 4. If the taxpayer is liable for any audit under this act?
Note: For FY 2017-18, it will contain details for July 2017 to March 2018 period.
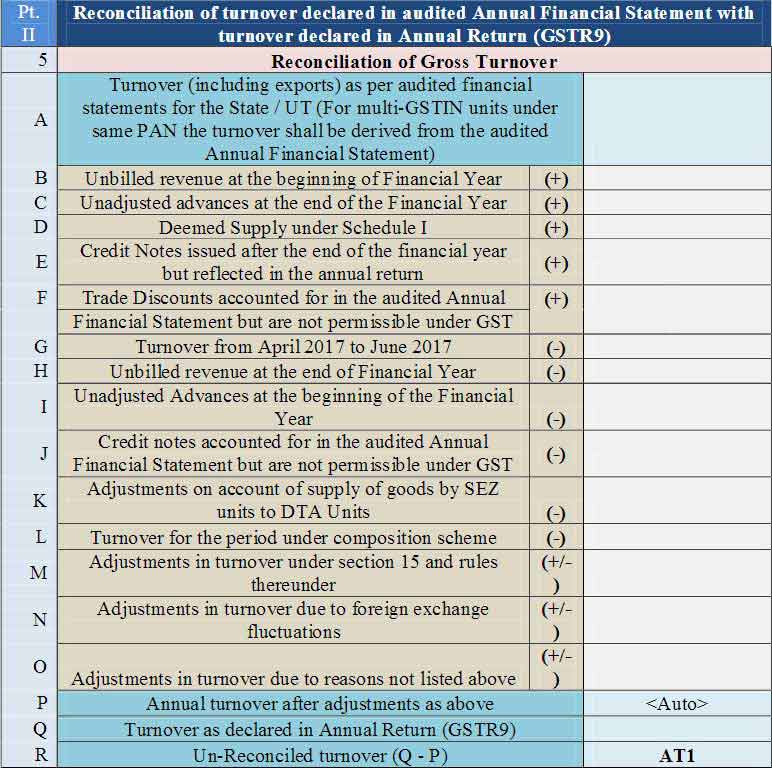
Part 2: Reconciliation of turnover declared in the audited Annual Financial Statement with turnover declared in Annual Return (GSTR9)
- 5. Reconciliation of Gross Turnover
- 5A. Turnover (including exports) as per audited financial statements for the State / UT (For multi-GSTIN units under same PAN the turnover shall be derived from the audited Annual Financial Statement): The turnover as per the audited Annual Financial Statement shall be declared here. There may be cases where multiple GSTINs (State-wise) registrations exist on the same PAN. This is common for persons/entities with a presence over multiple States. Such persons/entities will have to internally derive their GSTIN-wise turnover and declare the same here. This shall include export turnover (if any). It may be noted that reference to audited Annual Financial Statement includes reference to books of accounts in case of persons/entities having a presence over multiple States.
- 5B. Unbilled revenue at the beginning of Financial Year (+): Unbilled revenue which was recorded in the books of accounts on the basis of accrual system of accounting in the last financial year and was carried forward to the current financial year shall be declared here. In other words, when GST is payable during the financial year on such revenue (which was recognized earlier), the value of such revenue shall be declared here.
- C. Unadjusted advances at the end of the Financial Year (+): Value of all advances for which GST has been paid but the same has not been recognized as revenue in the audited Annual Financial Statement shall be declared here.
- D. Deemed Supply under Schedule I (+): an Aggregate value of deemed supplies under Schedule I of the CGST Act, 2017 shall be declared here. Any deemed supply which is already part of the turnover in the audited Annual Financial Statement is not required to be included here.
- E. Credit Notes issued after the end of the financial year but reflected in the annual return (+): an Aggregate value of credit notes which were issued after 31st of March for any supply accounted in the current financial year but such credit notes were reflected in the annual return (GSTR-9)shall be declared here.
- F. Trade Discounts accounted for in the audited Annual (+) Financial Statement but are not permissible under GST: Trade discounts which are accounted for in the audited Annual Financial Statement but on which GST was leviable(being not permissible) shall be declared here.
- G. Turnover from April 2017 to June 2017 (-): Turnover included in the audited Annual Financial Statement for April 2017 to June 2017 shall be declared here
- H. Unbilled revenue at the end of Financial Year (-): Unbilled revenue which was recorded in the books of accounts on the basis of accrual system of accounting during the current financial year but GST was not payable on such revenue in the same financial year shall be declared here.
- I. Unadjusted Advances at the beginning of the Financial Year (-): Value of all advances for which GST has not been paid but the same has been recognized as revenue in the audited Annual Financial Statement shall be declared here.
- J. Credit notes accounted for in the audited Annual Financial Statement but is not permissible under GST (-): an Aggregate value of credit notes which have been accounted for in the audited Annual Financial Statement but were not admissible under Section 34 of the CGST Act shall be declared here
- K. Adjustments on account of supply of goods by SEZ units to DTA Units (-): an Aggregate value of all goods supplied by SEZs to DTA units for which the DTA units have filed the bill of entry shall be declared here.Easy Guide to GSTR 9C GST Audit Form with Online Return Filing Process
- L. Turnover for the period under composition scheme (-): There may be cases where registered persons might have opted out of the composition scheme during the current financial year. Their turnover as per the audited Annual Financial Statement would include turnover both as for composition taxpayer as well as the normal taxpayer. Therefore, the turnover for which GST was paid under the composition scheme shall be declared here.
- M. Adjustments in a turnover under section 15 and rules thereunder (+/- ): There may be cases where the taxable value and the invoice value differ due to valuation principles under section 15 of the CGST Act, 2017 and rules thereunder. Therefore, any difference between the turnover reported in the Annual Return (GSTR 9) and turnover reported in the audited Annual Financial Statement due to the difference in valuation of supplies shall be declared here.
- N. Adjustments in turnover due to foreign exchange fluctuations (+/- ): Any difference between the turnover reported in the Annual Return (GSTR9) and turnover reported in the audited Annual Financial Statement due to foreign exchange fluctuations shall be declared here
- O. Adjustments in turnover due to reasons not listed above (+/-): Any difference between the turnover reported in the Annual Return (GSTR9) and turnover reported in the audited Annual Financial Statement due to reasons not listed above shall be declared here.
- P. Annual turnover after adjustments as above
- Q. Turnover as declared in Annual Return (GSTR9): Annual turnover as declared in the Annual Return (GSTR 9) shall be declared here. This turnover may be derived from Sr. No. 5N, 10 and 11 of Annual Return (GSTR 9)
- R. Un-Reconciled turnover (Q – P) AT1
- 6. Reasons for Un – Reconciled difference in Annual Gross Turnover
- Reasons for non-reconciliation between the annual turnover declared in the audited Annual Financial Statement and turnover as declared in the Annual Return (GSTR 9) shall be specified here.

- 7. Reconciliation of Taxable Turnover
- The table provides for the reconciliation of taxable turnover from the audited annual turnover after adjustments with the taxable turnover declared in annual return (GSTR-9).
- A. Annual turnover after adjustments (from 5P above): Annual turnover as derived in Table 5P above would be auto-populated here.
- B. Value of Exempted, Nil Rated, Non-GST supplies, No-Supply turnover: Value of exempted, nil rated, non-GST and no-supply turnover shall be declared here. This shall be reported net of credit notes, debit notes and amendments if any.
- C. Zero-rated supplies without payment of tax: Value of zero-rated supplies (including supplies to SEZs) on which tax is not paid shall be declared here. This shall be reported net of credit notes, debit notes and amendments if any.
- D. Supplies on which tax is to be paid by the recipient on reverse charge basis: Value of reverse charge supplies on which tax is to be paid by the recipient shall be declared here. This shall be reported net of credit notes, debit notes and amendments if any
- D1. Supplies on which tax is to be paid by the ecommerce operators as per section 9(5) [Supplier to report]
- E. Taxable turnover as per adjustments above (A-B-C-D-D1). The taxable turnover is derived as the difference between the annual turnover after adjustments declared in Table 7A above and the sum of all supplies (exempted, non-GST, reverse charge, supplies made through 9(5) etc.) declared in Table 7B, 7C, 7D and 7D1 above. This field shall be auto-calculated and non-editable
- F. Taxable turnover as per liability declared in Annual Return (GSTR9): Taxable turnover as declared in Table 4N of the Annual Return (GSTR9) shall be declared here.
- G. Unreconciled taxable turnover (F-E)

- 8. Reasons for Un – Reconciled difference in taxable turnover
- Reasons for non-reconciliation between the adjusted annual taxable turnover as derived from Table 7E above and the taxable turnover declared in Table 7F shall be specified here.

Part 3: Reconciliation of tax paid
- 9. Reconciliation of rate-wise liability and amount payable thereon
- 9A to 9O tax rates, others rate, interest, penalty, late fee and others
- The table provides for the reconciliation of tax paid as per the reconciliation statement and the amount of tax paid as declared in the Annual Return (GSTR 9). Under the head labelled ―RC‖, supplies where the tax was paid on a reverse charge basis by the recipient (i.e. the person for whom a reconciliation statement has been prepared ) shall be declared with the GSTR 9 file an annual return form with GSTR 9
- New field (K-2) added in Table 9.:- Supplies on which e-commerce operator is required to pay tax as per section 9(5) (including amendments, if any) [E-commerce operator to report]
- P. The total amount to be paid as per liability declared in Table 9A to 9O is auto-populated here. This field is non-editable. Value of new row 9 K1 & 9 K2 shall also be considered in the Total amount of 9P.
- Q. The amount payable as declared in Table 9 of the Annual Return (GSTR9) shall be declared here. It should also contain any differential tax paid on Table 10 or 11 of the Annual Return (GSTR9). The taxpayer can use the ‘system-generated summary based on GSTR 9’ PDF to fill this field.

- 10. Reasons for un-reconciled payment of amount: Reasons for non-reconciliation between payable / liability declared in Table 9P above and the amount payable in Table 9Q shall be specified Part-B: Certification.

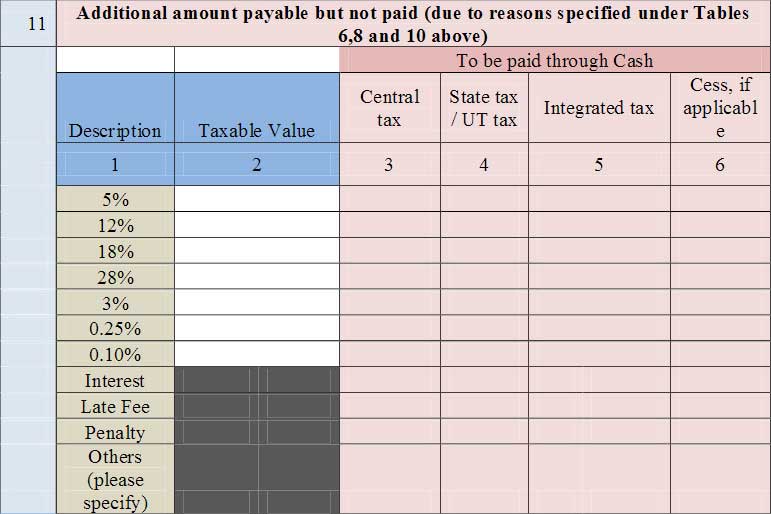
- 11. Additional amount payable but not paid (due to reasons specified under Tables 6,8 and 10 above): Any amount which is payable due to reasons specified under Table 6, 8 and 10 above shall be declared here.
- A new field (G2) added in Table 11:- Supplies on which e-commerce operator is required to pay tax as per section 9(5) (including amendments, if any) [E-commerce operator to report]
Part 4: Reconciliation of ITC (Input Tax Credit)
- 12. Reconciliation of Net ITC (Input Tax Credit)
- A. ITC availed as per audited Annual Financial Statement for the State/ UT (For multi-GSTIN units under same PAN this should be derived from books of accounts): ITC availed (after reversals) as per the audited Annual Financial Statement shall be declared here. There may be cases where multiple GSTINs (Statewise) registrations exist on the same PAN. This is common for persons/entities with a presence over multiple States. Such persons/entities will have to internally derive their ITC for each individual GSTIN and declare the same here. It may be noted that reference to audited Annual Financial Statement includes the reference to books of accounts in case of persons/entities having the presence over multiple States.
- B. ITC booked in earlier Financial Years claimed in current Financial Year (+): Any ITC which was booked in the audited Annual Financial Statement of an earlier financial year(s)but availed in the ITC ledger in the financial year for which the reconciliation statement is being filed for shall be declared here. This shall include transitional credit which was booked in earlier years but availed during Financial Year 2017-18.
- C. ITC booked in current Financial Year to be claimed in subsequent Financial Years (-): Any ITC which has been booked in the audited Annual Financial Statement of the current financial year but the same has not been credited to the ITC ledger for the said financial year shall be declared here.
- D. ITC availed as per audited financial statements or books of account: ITC availed as per audited Annual Financial Statement or books of accounts as derived from values declared in Table 12A, 12B and 12C above will be auto-populated here.
- E. ITC claimed in Annual Return (GSTR 9): Net ITC available for utilization as declared in Table 7J of Annual Return (GSTR9) shall be declared here.

- 13. Reasons for un-reconciled differences in ITC
- Reasons for non-reconciliation of ITC as per audited Annual Financial Statement or books of account (Table 12D) and the net ITC (Table 12E) availed in the Annual Return (GSTR-9) shall be specified here.

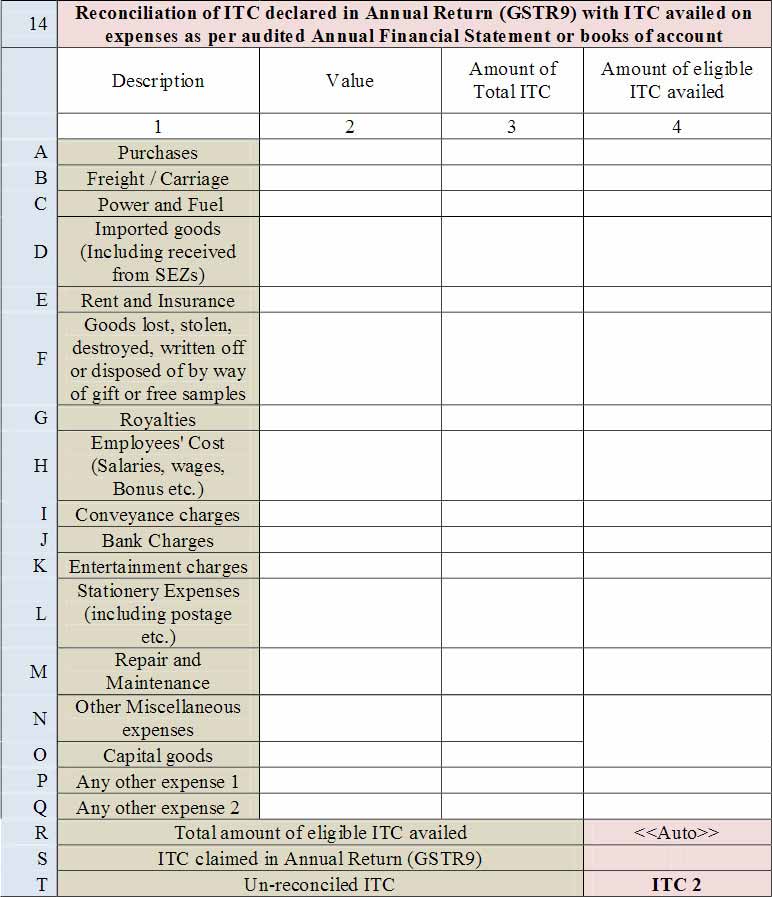
- 14. Reconciliation of ITC declared in Annual Return (GSTR9) with ITC availed on expenses as per the audited Annual Financial Statement or books of account.
- This table is for the reconciliation of ITC declared in the Annual Return (GSTR9) against the expenses booked in the audited Annual Financial Statement or books of account. The various sub-heads specified under this table are general expenses in the audited Annual Financial Statement or books of account on which ITC may or may not be available. Further, this is only an indicative list of heads under which expenses are generally booked. Taxpayers may add or delete any of these heads but all heads of expenses on which GST has been paid/was payable are to be declared here.
- A. Purchases
- B. Freight / Carriage
- C. Power and Fuel
- D. Imported goods (Including received from SEZs)
- E. Rent and Insurance F Goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift or free samples
- G. Royalties
- H. Employees’ Cost (Salaries, wages, Bonus etc.)
- I. Conveyance charges
- J. Bank Charges
- K. Entertainment charges
- L. Stationery Expenses (including postage etc.)
- M. Repair and Maintenance
- N. Other Miscellaneous expenses
- O. Capital goods
- P. Any other expense 1
- Q. Any other expense 2
- R. Total amount of eligible ITC availed: Total ITC declared in Table 14A to 14Q above shall be auto-populated here.
- S. ITC claimed in Annual Return (GSTR9): Net ITC availed as declared in the Annual Return (GSTR9) shall be declared here. Table 7J of the Annual Return (GSTR9) may be used for filing this Table.
- T. Un-reconciled ITC | ITC 2
- 15. Reasons for the un-reconciled difference in ITC: Reasons for non-reconciliation between ITC availed on the various expenses declared in Table 14R and ITC declared in Table 14S shall be specified here.

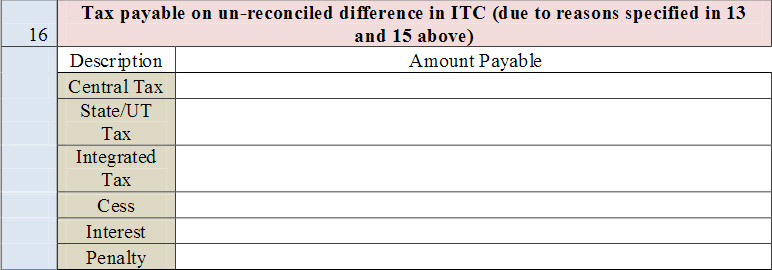
- 16. Tax payable on the un-reconciled difference in ITC (due to reasons specified in 13 and 15 above): Any amount which is payable due to reasons specified in Table 13 and 15 above shall be declared here.
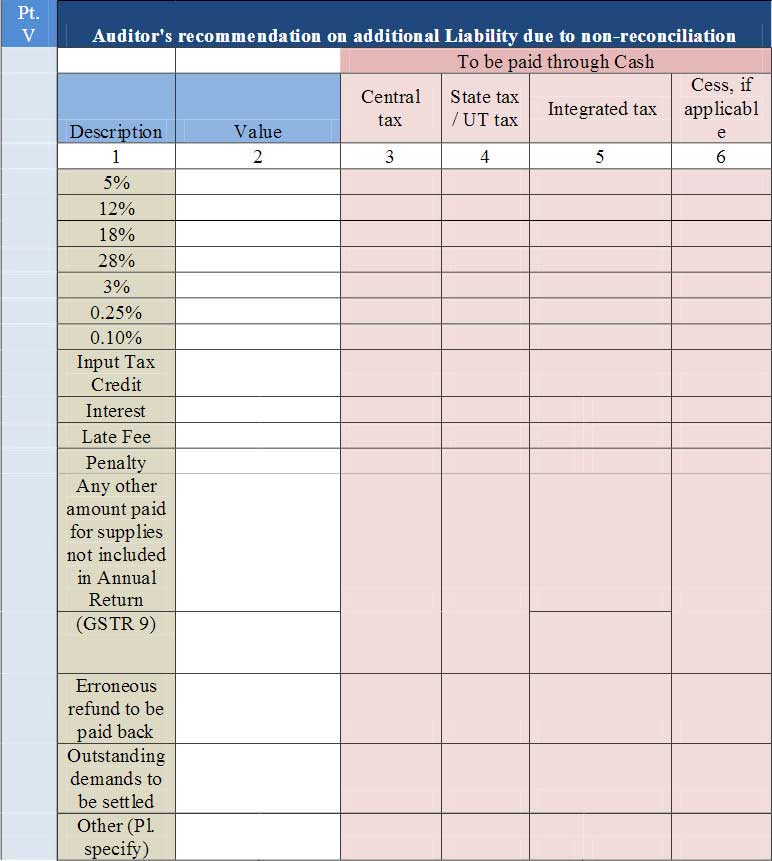
Part 5: Auditor’s recommendation on additional Liability due to non-reconciliation
- Part V consists of the auditor’s recommendation on the additional liability to be discharged by the taxpayer due to non-reconciliation of turnover or non-reconciliation of the input tax credit. The auditor shall also recommend if there is any other amount to be paid for supplies not included in the Annual Return. Any refund which has been erroneously taken and shall be paid back to the Government shall also be declared in this table. Lastly, any other outstanding demands which are recommended to be settled by the auditor shall be declared in this Table.

GSTR 9C Part-B: Certification
A certification part is also done once after the GSTR 9 audit is conducted by the person responsible for the audit. The form has two major parts including
1 – Certification in cases where the reconciliation statement (Form GSTR 9C) is drawn up by the person who had conducted the audit.
- A – Balance sheet date
- B – P&L Account including dates
- C – Cash flow statement including dates
2 – Based on audit the auditor mentioned:
Proper maintenance of books status
Or not maintained

3(A) – Based on any observations done by the auditor, reporting any differences:
3(B) – Further reporting
4 – Documents required under section 35(5) of CGST and reconciliation statement required which are to furnished under section 44(2) of CGST Act annexed in form no. GSTR 9C
5 – All the details and transactional information stated in GSTR form 9C are validated in this point.
Credentials With Signature, Name of the signatory, Membership no. and Date

General Queries on GSTR 9C Form
Q.1 Is the Audit of Accounts maintained by the registered taxable person required to be got done by a Chartered Accountant/Cost Accountant under GST?
As per the GST law, it is mandatory for all the Registered person to get their accounts audited by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant whose aggregate turnover during a financial year exceeds the threshold limit of Rs. 5 Crore. Whence, no such audit is required to be got done by the Chartered or Cost accountant in cases other than mentioned above.
Q.2 – Does ‘aggregate turnover’ deals with topics such as stock transfers/ cross charges effected between branches located in two different states?
Aggregate Turnover has been defined in Section 2(6) of CGST/ SGST Act and the definition of aggregate turnover includes ‘inter-state supplies of a person having the same PAN’. Thus, we see that stock transfers/ cross-charges of services provided from a branch, located in one state to a branch located in another state is included in the definition of Aggregate turnover of the related branch supplying goods/ services.
Q.3 – Does the term ‘aggregate turnover,’ includes stock transfers which are effective within the States having same GSTIN for determining the threshold limits?
The term ‘aggregate turnover’ is not supposed to be included in stock transfers effective within the same state having single GSTIN for the purpose of determining the threshold limit. However, in cases where more than one GSTIN has been allotted for the different branches located in the same state, such branch transfers shall be included for computing threshold limit of Rs. 5 crore to get to the conclusion that whether there is any requirement for audit or not.
Q.4 – Will a Registered Taxpayer who has exclusively exempted supply of goods or services exceeding Rs. 2 crores, would require to fill the GSTR 9C form?
As ‘aggregate turnover’ has been defined under the GST Act, it includes ‘exempt supplies’. Thus, even in the case of a registered person under GST who provides exempted supplies, will have to file Form GSTR 9C.
Q.5 Does the Form GSTR 9C be required to be filed by a person against each registration obtained by him in respect of each of the States?
Provision is that Section 35(5) of SGST Act requires Audit to be conducted in addition to Section 35(5) of CGST Act. Thus, to maintain Compliance audit is required to be conducted state wise as per Section 35(5) of SGST Act. Thus, if we consider an example like if a person is having registration in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, then he is required to be audited for his accounts under KGST Act, 17 and TNGST Act, 17. The GSTR 9C form is required to be filed under Rule 80(3) of KGST Rules, 2017 and the TNGST Rules. Thus, it is evident that a person registered in more than one state is supposed to file form GSTR 9C registration wise for each and every state.
Q.6 – Is it required for a Chartered Accountant to be got registered as a GST practitioner to get certified the Form GSTR 9C?
A GST practitioner gets authorization for the practice of the below-mentioned rules as per Section 48 of the CGST/ SGST Act under Rule 83(8) of the CGST/ SGST Act:
- a) furnishing the details of outward and inward supplies
- b) to furnish monthly, quarterly, annual or final return
- c) Can make deposits to get amount credited into the electronic cash ledger
- d) he could file a claim for any sort of refund
- e) filing application for getting the registration amended or getting the registration canceled
The GST Act/ Rules does not give the ‘Power to Audit’ to a GST practitioner as per section 35(5). ‘Power to Audit’ is only granted to Chartered Accountants or Cost Accountants. Thus, it is not required for a Chartered Accountant to get registered as a GST practitioner for certifying Form GSTR 9C.
Q.7 – What are the documents to be enclosed along with GSTR 9C?
- Under section 35(5), it is stated that a copy of audited accounts and other such documents in the prescribed manner along with the reconciliation statement (Form GSTR 9C) to be submitted.
- The ‘Prescription’ which is mentioned in the Act should be provided as mentioned in the term ‘as may be prescribed’. Only the audited annual accounts have been prescribed in Rule 80(3) in the name of documents.
- Talking about Part B of GSTR 9C, it is required by the GST Auditor to get a copy of audit report of the entity enclosed where the audit of the entity has been conducted by another person under a statute other than the GST Act.
- In the mentioned case, the documents which has been declared by the statute, which would further be considered as audited financial statements, must be annexed to the audit report.
Q.8 – Should the Form GSTR 9 and Form GSTR 9C get filed separately?
As per Section 44(2) of the CGST/ SGST Act 2017, a Registered person is required to file his Annual return in Form GSTR 9 along with this he has to provide a reconciliation statement through Form GSTR 9C. Thus we see, Form GSTR 9C is required to be filed along with Form GSTR 9 where the turnover exceeds Rs. 2 crores.
Q.9 – Is there any time limit to file Form GSTR 9C?
The Section 44(2) states that the reconciliation statement is required to be provided in Form GSTR 9C along with the Form GSTR 9. Section 44(1), on the other hand, declares the due dates. As per this section, the due date for filing the annual return is on or before the thirty-first day of December following the end of the FY for which the Annual return is prepared. Thus, the conclusion could be drawn that the due date for filing reconciliation statement in Form GSTR 9C is on or before the thirty-first day of December following the end of the financial year for which the reconciliation statement is being prepared.
Q.10 – Could the late fee be waived off in Genuine and special cases?
The Government has the right to get a part or full of the late fee, mentioned in section 47, waived through notification, for such section of taxpayers and under such mitigating and specified circumstances. All this could be done on the recommendation of the Council. However, no such notification is evident to till date issued by the Central Government/ State Government.
Q.11 – Is Audit, mentioned under Section 35(5), be applicable to the Non-Filers or unregistered Persons who are liable to get registered?
- As per Section 35(5) of the CGST Act, only a Registered person is required to get his accounts audited by a CA or CWA. Again, a non-filer is a Registered Person according to Section 25 of the CGST Act, thus he must get audit conducted under Section 35(5) of the said Act. Considering practically, such a person would never had filed his returns and hence, Form 9 & 9C wouldn’t be possible in his case and no audit for him is required.
- Understanding clearly, an unregistered person who is eligible for registration under Section 25 of the CGST is a taxable person. Here, the unregistered Person is not a Registered Person as per Section 2(94) of the CGST Act 2017. Hence, following Section 35(5) of the Act, audit is not required.
Q.12 – Mention the records which are required to be reconciled in Form GSTR-9C?
The records to be reconciled in GSTR-9C are:
- Books of accounts of the registered person – If a registered person has multiple registrations, The required information could be derived from the Audited financials of the entity.
- Annual Return of Registered Person in Form GSTR 9.
Q.13 – What are the contents of Form GSTR 9C?
Form GSTR 9C consists of 2 parts. Part-A consists of Reconciliation statement and Part B is Certificate to be issued by GST Auditor.
Q.14 – What are the details which are to be provided in SI. No.5B (Unbilled revenue at the beginning of Financial Year)?
The unbilled revenue at the beginning of Financial Year are required to be added in Clause 5B. The unbilled revenue recorded on the basis of the accrual system of Accounts in the Books of accounts for the earlier financial year for which the invoice is issued under GST law, is required to be declared here. Understanding more clearly, the value of such Revenue which has been recognized as income during a financial year on which GST is liable to be paid, is required to be mentioned in SI. No.5B
Q.15 – Mention the adjustments to be included/excluded from SI. No.5C of Form GSTR-9C?
The advances which are received could be of various purposes. Therefore, the Advances on which GST is liable should only be considered for the adjustment. The illustrations of advances to be included/excluded are as follows:
Include for Adjustment
| 1. | Advance received in respect of services for which the supply has not been made as on 31st March 2018 | Revenue not recognized in books, but offered to tax for GST |
| 2. | Advance received for Goods before 15th Nov 2017 and the supply of goods not complete as on 31st March 2018 | Revenue not recognized in books, but offered to tax for GST |
Do NOT include for Adjustment
| Sl. No. | Particular’s | Reason |
| 1. | Advance received for EXEMPTED services as on 31St March 2018 | GST is not applicable |
| 2. | Advance received for Goods after 15th Nov 2017 | GST is not applicable |
| 3. | Financial Advances received which are not adjustable against any services | NOT a GST Transaction |











IN 9C TABLE 14 WE NEED TO PUT ONLY EXPENSES ARE OPENING BALANCE ALSO WE NEED TO PUT HERE
Total Expenses during the year have to be mentioned there
Where should credit notes of 17-18 passed in Year 18-19 be shown in GSTR 9/9C of 2018-19?
Thanks
It should be shown in the year 2017-18, not in 2018-19
I want to know the Total Turn over above 5 cors including the credit note for the financial year 2018-2019. Credit note 79 lacks.Then GST Audit is compulsory. But the question is my credit note will be tax@18%.
Yes
Sir, if i claimed excess input in gstr-3b but in annual return GSTR-9 We have claimed the same input as in Books of accounts so please tell me in GSTR-9C were to report this Difference.
In table no. 12 and in the Auditors report
Sir,
Is there any additional benefits given by govt. if we fill 9C with having turnover more than 2 Cr but less then 5Cr?
if yes, than what are the benefit?
No such benefit is available from portal site
God evening
I would like to ask a query that in my office we filed one of our clients GSTR9C without any reconciliation and now what is the solution would you give for this problem
can we submit the correct 9C form manually in the GST office? and what are the consequences we need to face?
Please suggest the solution
Thank you
GSTR-9C once filed and it can not be amended
Respected Sir,
Whether we have to consider the Discount & Incentive in aggregate Turnover for GSTR-9C?
No
Can you tell me, how to put in excise duty claimed amount in GSTR 9C, where is the put in the table
Column 12B in GSTR 9C “ITC booked in earlier financial years claimed in the current financial year”
Can you help in configuring a laptop to generate GSTR 9C JSON file on a chargeable basis ?
We are getting errors in uploading GSTR 9C. error is ” auditor signature Invalid ” query is raised on the portal but no help. Is there anybody who can do the job for us on charge
Please attach signature of auditors which is registered on GST portal.
How to get the button named get the client?
Please specify in detail
HOW TO SHOW RCM ITC (ON TRANSPORT) IN GSTR – 9C?
Sir, Please tell me about GSTR 9C due to filling
Due date is 31.08.2019
I have nil return & no input in Jan, Feb & Mar 2017-18 is it compulsory to file GSTR 9C reconciliation statement for me
GSTR-9C IS REQUIRED TO BE FILED ONLY IN CASE YOU ARE LIABLE FOR AUDIT UNDER GST.
Sir, part II -5, (E), a credit note issued after the end of the fy but reflected in the annual return,
-_———-
We have declared credit note, issued in 17-18, under Part-II 4-(I), of Gstr9
And credit notes issued in next year 18-19, declared in Part V- 11, of Gstr9,
——–
We are confused, about point II -5, (E),
Please clarify … thanks
Part II- 5 (E) covers NIL rated supplies. so please clarify your query.
Very good efforts has been made by you and it is very useful material.
Sir, Can you please explain where to file GSTR 9C?
GSTR-9C is still not released by dept. on portal.
Painstaking efforts by you.
Is it an Audit Report or a Reconciliation Statement?
Can you provide Excel format of 9C?
There is no excel format of GSTR-9C yet. A pdf is made available by Govt. which shall be available on CBIC, gov, in under Notification No. 49/Central Tax dated 14.09.2018.