In the series of GSTR return form filing, we have already discussed the procedures for filing GSTR-1, GSTR-2, GSTR-3, and GSTR-4; this is GSTR-5 for the person registered under GST and is a non-resident. It requires the detailing of inward and outward supplies from the business. The eligible taxpayers can view and download the GSTR 5 form in PDF format file here.
Non-Resident Foreign Taxpayer: The non-resident foreign taxpayers not owning a business in India but making supplies in the country for a short period of time is liable to pay tax under GST. They need to pay tax, interest, fees, and penalty within 20 days after the tax period ends or after 7 days of the validation period of registration, whichever is earlier of the two dates.
- Who Required to File GSTR 5?
- GSTR 5 Return Filing Due Date
- Penalty Missing the GSTR 5 Due Date
- How to File GSTR 5 Form Online?
- General Queries on GSTR 5 Form
Latest Update in GSTR 5
- “CBIC new notification to extend the due date for furnishing FORM GSTR-5 for the month of December 2024”. read PDF
- “New Advisory on Reporting of supplies to un-registered dealers in GSTR1/GSTR 5. This functionality is currently under development.” View more
- “CBIC shared the latest update about upcoming functionalities for the taxpayers on the GST official portal in July 2021 month.” Read PDF
- “Forthcoming advanced functionalities for taxpayers on the GST portal related to GSTR 4, GSTR 1, composition taxpayers, etc.” Read more
- “Extension in dates of various GST Compliances for GST Taxpayers” Read more
Features of GSTR 5 Return Form
- A non-resident foreign person can enroll under GST through a temporary registration for a specific validity period
- This is the GST return form for registered non-resident foreigners doing business in India
- The GSTR-5 form can be filed from a Facilitation Centre or directly by the taxpayer
- The details of outward and inward supplies will be furnished in a single form
- GSTR 5 is to be filed and the tax (including the penalty, fees, interest, etc.) is to be paid every month (for the registration period) by the 20th of the next month for a particular tax period or within seven days after the end of the validity period of registration
GSTR 5 Eligibility – Who Should File It?
- The GSTR 5 return form is to be filed by a non-resident foreign taxpayer who is registered under GST and makes a supply of OIDAR services (Online information and database access or retrieval services) from outside the country to a non-taxable person in India
- Such a person can acquire a temporary registration through the GST portal and file returns for the supplies made by him for a specific tax period. The person should not have a business establishment in India
Due Date (Deadline) for Filing GSTR 5 Return
The due date for the GSTR-5 return form was the 20th of the month following a particular tax period. However, after Budget 2022, the due date is now the 13th of the following month.
GSTR 5 due date schedule is as follows:
| Month | Due Date |
|---|---|
| February 2026 | 13th March 2026 |
| January 2026 | 13th February 2026 |
| December 2025 | 13th January 2026 |
| November 2025 | 13th December 2025 |
| October 2025 | 13th November 2025 |
| September 2025 | 13th October 2025 |
| August 2025 | 13th September 2025 |
| July 2025 | 13th August 2025 |
| June 2025 | 13th July 2025 |
| May 2025 | 13th June 2025 |
| April 2025 | 13th May 2025 |
| March 2025 | 13th April 2025 |
| February 2025 | 13th March 2025 |
| January 2025 | 13th February 2025 |
| December 2024 | 15th January 2025 |
Note: The due date for the issue of notification, notice, sanction order, approval order, filing of the appeal, statements, furnishing of return, reports, applications, or any type of documents is most likely going to extend to 30th June 2020. Along with documents, the due dates for any compliance with GST laws which are expiring between 20th March 2020 to 29th June 2020 shall be stretched up to 30th June 2020. Read Press Release
Interest on Late Payment of GST & Penalty of Missing the GST Return Due Date
GST Council Stated that on every late payment of tax it is a provision of 18 per cent tax rate to be annually charged on the tax of GST from the due date until the tax has been paid wholly. The guidelines in detail are in chapter 10, 50th point: https://cbec-gst.gov.in/CGST-bill-e.html
For example – The taxpayer missing the deadline in the payment of GST taxes will be paying a calculative tax rate from the start of the due date i.e 1000*18/100*1/365= Rs. 0.49 per day approximately.
(Rs. 1000 is the tax payment) (18% per annum is the calculative interest rate) (1 day is delayed time by the taxpayer)
In case if a taxpayer does not file his/her return within the due dates mentioned above, he shall have to pay a late fee of Rs. 50/day i.e. Rs. 25 per day in each CGST and SGST (in case of any tax liability) and Rs. 20/day i.e. Rs. 10/- day in each CGST and SGST (in case of Nil tax liability) subject to a maximum of Rs. 5000/-, from the due date to the date when the returns are actually filed.
Step by Step Procedure to File GSTR-5 Form Online
Table 1&2: Details of Taxpayer
- GSTIN: GSTIN stands for Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number. The GSTIN is a 15-digit number that includes a 2-digit state code, a 10-digit permanent account number, and 3-digit includes state, future use, and check-digit. It is auto-populated when we file returns
- Name of the Taxpayer: This is the name of a Non-resident taxpayer owning a business outside of India and supplying goods and services. This field is also auto-populated at the time of return filing
- Address: The business address of the taxpayer is auto-populated at the time of return filing
- Month-Year: The taxpayer requires to choose the date from the drop-down for which month and year GSTR-5 is being filed
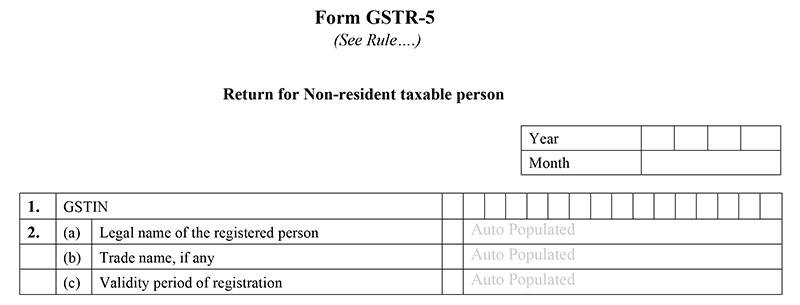
Table 3: Imported Goods Details
- Goods Imported: All the goods imported into Indian territory need to mention in this category. Taxpayers have to fill HSN(Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code and other descriptions which are asked
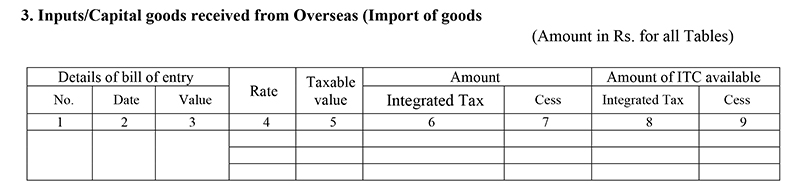
Table 4: Modification To The Imported Goods Details
- Changes to Goods Imported: Changes regarding imported goods of an earlier period should be updated in this head. Any IGST rate change and bill of entry changes are covered under this
Table 5: B2B outward supplies
- Outward Supplies: The detailing of supplies made outside of India by Foreign taxpayers should be covered in this head. The description must include IGST, CGST, and SGST charged
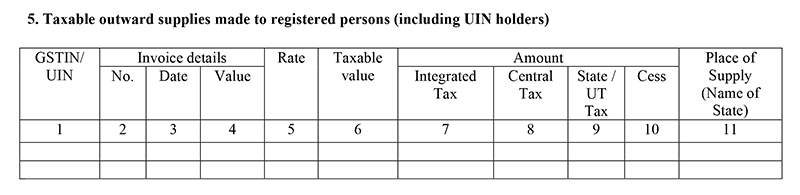
Table 6: B2C Inter-state supplies where supply exceeds more than Rs. 2.5 lakh
- Inter-state supplies only more than 2.5 lakh – This head covers all the interstate supplies made by a registered person to an unregistered person where the supplies should be more than Rs. 2.5 lakh
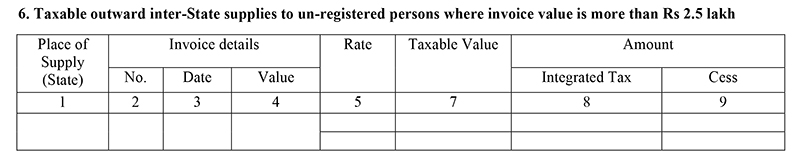
Table 7: Supplies other than those mentioned in the above head to an unregistered person
- The supplies from B2C which exceeds Rs. 2.5 lakh should be covered in above head and the supplies under Rs. 2.5 lakh from a registered person to an unregistered person are covered in this head. All the details are furnished by invoices issued at the time of supplies
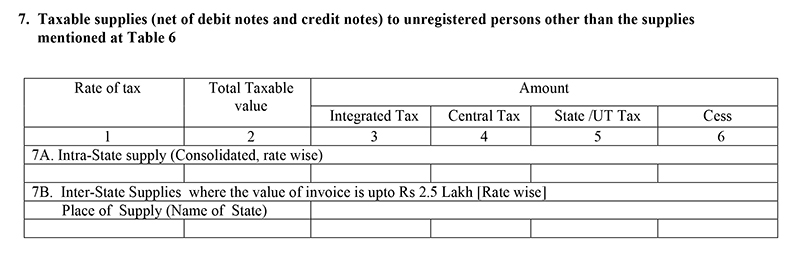
Table 8: modification to the B2B outward or B2C inter-state supplies
- If there is any modification in the table-5 and table-6 from previous tax periods, the changes are updated in this head
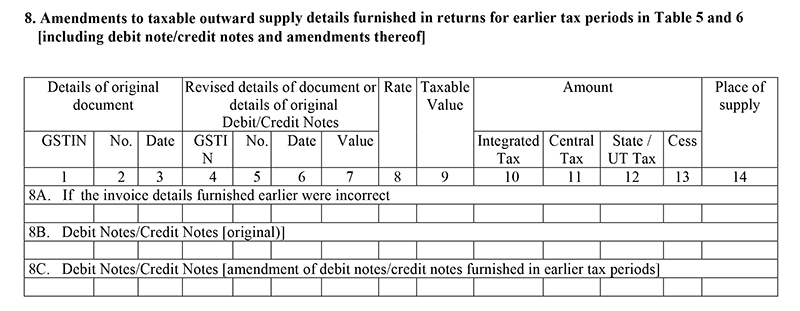
Table 9: modification to table-7
- Any modification to table-7 where a registered person supplies to an unregistered person( if the supplies are under Rs. 2.5 lakh) to the previous tax period is done under this heading
Table 10: total Payable liability
- Payable Liability: The information is auto-populated from the above headings and shows the final GST liability. Here the taxpayer gets the separate tax liability against IGST, CGST, and SGST.
Table 11: Total Tax Paid
- Tax payable or paid: This head includes the detailing of the total tax paid under IGST, CGST, and SGST during the tax period. This information is auto-populated from the details given in the above headings
Table 12: Interest and late fees payable or paid
- The heading is concerned about the interest, late fee and any other amount is payable or paid under CGST, IGST, and SGST
Table 13: Refunds claimed
- Refunds: This field is auto-populated if any refund amount received from Electronic Cash Ledger
Table 14: Debit entries
- Debit entries for tax and interest paid – When the tax is paid and the return is successfully submitted, this information about the debit entries for tax and interest payment is auto-populated
After completing the details, the taxpayer needs to electronically sign the form for authentication that the furnished details are true.
General Queries on GSTR 5 Form
Q.1 – What is GSTR-5?
All Non- Resident Taxpayer unwilling to avail ITC on local procurements need to file GSTR-5 return. In case the taxpayer wishes to avail ITC on local procurement he is required to get registered as a normal taxpayer and file GSTR-1/ 2/ 3 as a normal/casual taxpayer.
Q.2 – Till when GSTR-5 could be filed?
The GSTR-5 return is to be filed by the non- Resident Taxpayers for the time period for which they have got registered. The form is required to be filed within seven days after the expiry date of registration. In such a case where the registration period is for more than a month, a monthly return needs to be filed by 20th of the month following the tax period. In continuation of this return for the remaining period is required to be filed within a period of seven days.
Q.3 – How can I access to GSTR-5?
After logging in to the Returns Dashboard by the taxpayer, GSTR-5 could be easily accessed on the GST Portal.
- Let’s know the path below:
- Services > Returns > Returns Dashboard
Q.4 – Is there any Offline Tool available for GSTR-5 filing?
No offline tool is available for GSTR-5 filing.
Q.5 – Mention the pre-conditions for filing GSTR-5?
The Pre-conditions for the filing of GSTR-5 are:
- The taxpayer is required to be registered as a Non-Resident taxable person and should be having a valid GSTIN.
- The Taxpayer needs to be having his valid User ID and password.
- The digital signature is made mandatory for taxpayers like Companies and LLP/FLLP. Such taxpayers are required to be having a valid & non-expired / non-revoked Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). In cases other than these, authentication of return could be done through EVC.
Q.6 – In the case of a Non – resident taxpayer, is there an Electronic Cash Ledger/ ITC/ Tax Liability Register available?
Yes, for a non- Resident Taxpayer also Electronic Cash Ledger/ ITC/ Tax Liability Register are maintained.
Q.7 – What all actions could be taken regarding the invoice data auto-populated in GSTR-5?
Regarding the invoice data auto-populated in GSTR-5, the following actions could be taken:
- Accept
- Reject
- Pending for future Action
Note: Pending for action, option, is not available with the last/ final return.
Q.8 – What is the complete procedure after Form GSTR-5 is filed?
After the Form GSTR-5 is filed:
- On the successful submission of the Form GSTR-5, an ARN is generated.
- The Taxpayer is informed regarding the successful filing of the form via SMS and an email on his registered mobile and email id resp.
- The Form GSTR-6 could be successfully submitted without any hindrance or obstacle if GSTR-5 form is filed prior to it.
- Once the Form GSTR-5 gets submitted getting DSC or E-sign or EVC affixed as the case may be, the Form is passed on to:
- The CBEC (Central Board of Excised Customs – the central tax authority
- Tax authority of jurisdictional State or UT
Q.9 – What are the modes of signing GSTR-5?
The GSTR-5 could be signed using DSC or EVC.
Q.10 – Can one preview the Form GSTR-5 before submitting?
Yes, Form GSTR-5 could be previewed before submission on the GST Portal.
Q.11 When can I claim the refund?
The refund could be claimed from the Electronic Cash Ledger in the last refund only and the last refund would be decided after considering the extended period of registration. The refund from the Electronic Cash Ledger could be done in case the liability register have zero balance across all the major and minor heads.
Q.12 – Is there any provision under which credit could be claimed against the taxes which have been paid on the import of services from outside India?
A Non-resident taxpayer is not liable to claim a credit on taxes paid against the import of services from outside India.