GSTR 2 is a tax return form that is used for filing the details of inward supplies of goods or services for taxation purpose. The form will be filled online on the GST portal after registration. Each registered recipient will have to file GSTR 2 furnishing details of inward supplies (purchases and imports) of goods and services made by him in a particular month. GSTR 2 is to be filed on or before the 15th of the next month. For example, the GSTR 2 form for the current month will be filed by 15th of next month.
The interesting part is that most of the columns in GSTR 2 will autofill with the details provided by your supplier in his GSTR-1 return form. You can review the information, accept or reject, edit if necessary, add remaining details in your GSTR 2 form, leave open (for pending supplies), and submit.
All Features of GSTR 2 Form
- GSTR 2 is a GST tax return form
- It is used to input the details of inward supplies (purchases) under GST
- The form is to be filed by the 15th of the next month for a particular tax period
- GSTR 2 is required to be filed only by the registered recipients of goods/services
- It will also contain the details of the imports made during the particular period
- The recipients can also use this form to claim ITC on previously paid taxes
- Most of the details in the GSTR 2 form of a recipient can be auto-populated with the information provided by the counterparty supplier in his GSTR-1 return
GSTR 2 Eligibility – Who all have to Submit this Return?
- The GSTR 2 return is required to be filed by all the normal GST registered taxpayers whether or not any inward transactions (purchases) of goods and/or services were made for the particular tax period
- GST composition registered dealers do not have to file GSTR 2 return
Note: The transaction date will be the date mentioned on the tax invoice.
Deadline for GSTR 2 Form Filing
In normal cases, the deadline for filing GSTR-2 is 15th of the next month for a particular tax period, however, the filing of GSTR-2 has been suspended until March 31, 2018, by the Committee of Officers. The detailed schedule shall be updated soon.
<!–GSTR 2 return will be filed monthly on the 15th of the next month by all the normal GST registered taxpayers. The due-dates for upcoming GSTR 2 return filing are as below.
- For July 2017 – 30th November 2017 (Revised Due Date)
- August 2017 –
–>
Interest on Late Payment of GST & Penalty of Missing the GST Return Due Date
According to The central Goods and Services act, if the person accidentally or purposely missed out the date to pay tax, GST Council has right to charge interest on late payment of taxes. The interest is 18% per annum and it depends on total missed out days as well. Read out the chapter 10 and point 50 to get the full information here: https://cbec-gst.gov.in/CGST-bill-e.html
This is how the calculation of the late tax payment take place: 1000*18/100*1/365 = 0.49 Rs. per day. Here (1000Rs. Is the liable tax amount) (interest rate per annum is 18%) (the total missed out days are 1 in this case)
In case if a taxpayer does not file his/her return within the due dates mentioned above, he shall have to pay a late fee of Rs. 50/day i.e. Rs. 25 per day in each CGST and SGST (in case of any tax liability) and Rs. 20/day i.e. Rs. 10/- day in each CGST and SGST (in case of Nil tax liability) subject to a maximum of Rs. 5000/-, from the due date to the date when the returns are actually filed.
Mandatory Instructions While Filing GSTR 2 Form
- Always take care while entering tax details and related figures as the amendment in GSTR form is a complex procedure with fine and penalties.
- Cross check the details with original invoice and receipts (only purchase) while tax data input
- Check for stable internet connection while uploading forms
- It is advisable to file the return within specified deadline and avoid late penalty
- Concern with your CA while filing any GSTR form for better compliance
Here’s the Step by Step Procedure for Filing GSTR 2 Form Online
Table 1 and 2: Taxpayer details
This table will contain the following details:
- Month, Year: The exact month and year for which the tax return is being filed
- GSTIN: GST Identification number of the registered recipient which will be auto-populated based on your GST registration. It is a unique 15-digit PAN-based number
- Legal name of the registered person: Name of the registered person will be present in this column
- Trade name: Name of the business, if any
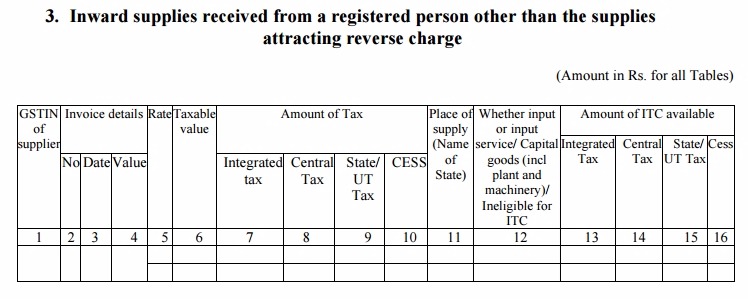
Table 3: Inward supplies received from a registered person other than the supplies attracting reverse charge
- This head will include details of all the purchases from a registered person, except the ones attracting the reverse charge. The information here will be auto-filled based on the details submitted by your registered supplier in his GSTR-1 form. You can review, edit and add the missing details and upload invoices if missing
- The recipient also needs to mention the applicable rate and amount of GST, whether the supply is eligible for input tax credit, and the ITC amount
- The details in certain cases might not be auto-populated if the seller did not file the relevant GSTR-1 or missed a transaction. Then, the buyer can manually enter the details of such transaction which will reflect in the GSTR-1A return of the seller
- If a particular supply is received in installments, then the buyer will have to mention its details in the return of the month in which the last installment is received as per the book records
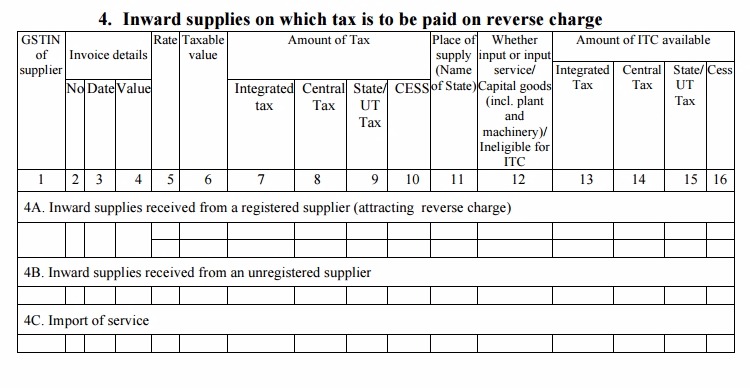
Table 4: Inward supplies on which tax is to be paid on reverse charge
- This table will contain the details of all the inward supplies (purchases) received from a registered or unregistered person in a particular month on which tax is levied on reverse charge basis, i.e., the buyer will have to pay GST direct to the government. This will include all the supplies with value over Rs. 5,000 from an unregistered supplier
- Table 4A will auto-fill based on the information provided by your registered supplier. It will contain all purchases from registered supplier on which reverse charge tax is applicable as per GST law
- 4B will contain the details of supplies with value over Rs. 5,000 made by an unregistered supplier
- 4C will contain details of important supplies which attract reverse charge
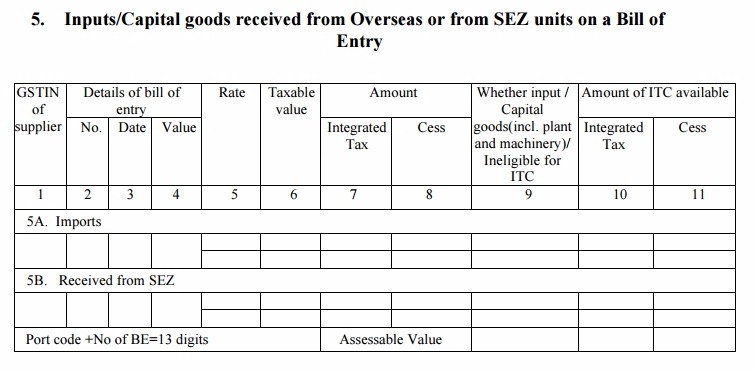
Table 5: Inputs/Capital goods received from Overseas or from SEZ units on a Bill of Entry
- The recipient will have to enter the details of all the Capital goods received by him from a person Overseas or from SEZ units on a registered bill of entry. He will also provide the bill of entry number and port code details along with ITC information, if applicable. IGST will be calculated in addition to custom duties on the import value
- 5A will have the details of all imports of capital goods and other inputs along with the Bill of entry, Port codes and bill numbers
- 5B will be used to furnish the details of goods received from a SEZ seller
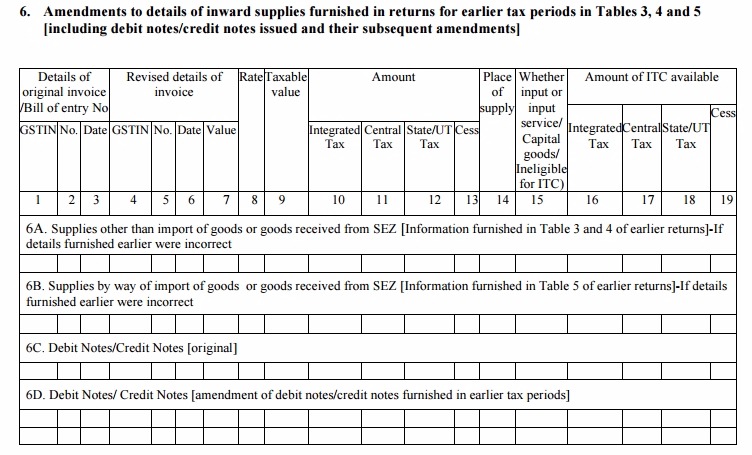
Table 6: Amendments to details of inward supplies furnished in returns for earlier tax periods in Tables 3, 4 and 5 [including debit notes/credit notes issued and their subsequent amendments]
- This head will contain the details of changes (if any) to be made in the inward supply details provided in the earlier tax period returns. This will include the original debit/credit notes and the details of their subsequent amendments
- The changes in GSTR 2 after successful filing for a particular month can only be made while filing GSTR 2 of the following month. The respective seller will also receive the notification of these changes through his GSTR-1A return and will have the option to accept or modify it
- Head 6A will contain details of revisions/changes in inward supplies (purchases) of all types except imports and SEZ supplies
- 6B will have the details of revisions in inward supplies received through imports or from SEZ
- 6C will include the original debit/credit notes for the purchases made in the past month for which revisions are being made
- 6D will contain the details of the changes to be made in debit/credit notes of the past months
Note: GSTIN is not applicable for export of goods and services.
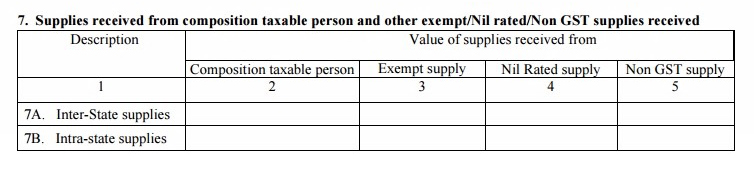
Table 7: Supplies received from composition taxable person and other exempt/Nil rated/Non-GST supplies received
- The details of the supplies received from a GST composition registered person or supplies that are GST exempted or zero-rated will come in this table. The composition supply information should auto-fill based on the details, easy Guide of Filing GSTR 2 Form for Inward Supplies provided by your supplier in his GSTR 4 form
- Supplies of certain items like petrol, diesel, etc. are non-GST supplies. The user needs to enter both inter-state and intra-state supplies information here separately for each category
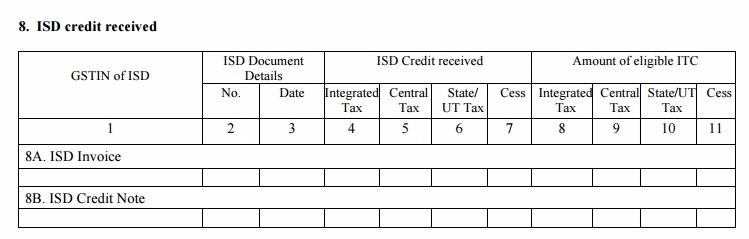
Table 8: ISD credit received
- It will contain the information of the input credit received by you from a registered Input Service Distributor (ISD) on the imports. Such credits will be fully available for the use of the recipient and will determine his eligibility to claim ITC
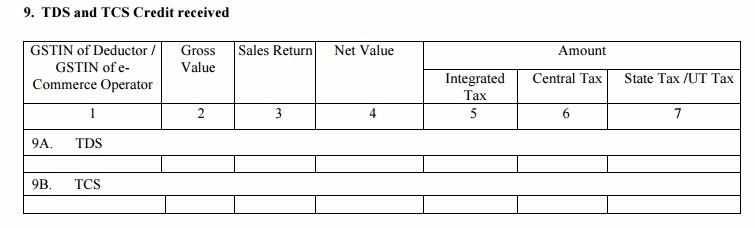
Table 9: TDS and TCS Credit received
- This table head will contain the information of the TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) if received by you on any eligible transaction. The information here will auto-populate from the deductor’s GSTR-7 Form. The TDS such received will be paid to the government. Sales return and Net value will not be required for TDS
- Details of the TCS received by e-commerce marketplaces on the payments made to the seller will be available here. The details will be auto-populated here from GSTR-8 Form of the e-commerce operator
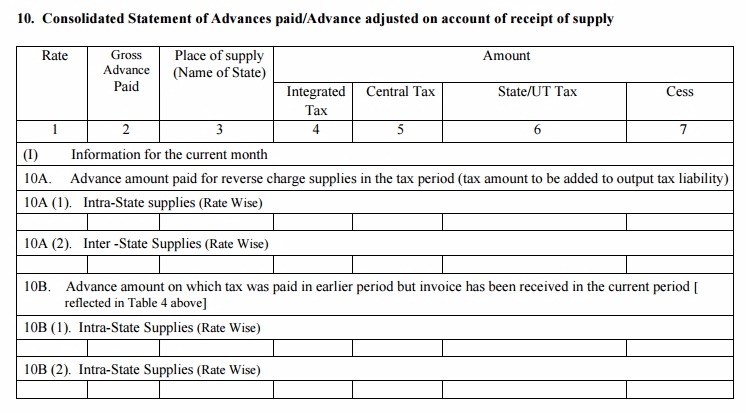
Table 10: Consolidated Statement of Advances paid/Advance adjusted on account of receipt of supply
If you paid any advance amount with respect to a particular supply this month and has an invoice for the same or made payment in an earlier tax period but received invoices only this month, the information and statements of the same will be furnished with this table.
This will include the advance paid for reverse charge supplies and the tax paid on such advance amount. For reverse charge supplies, the buyer will issue the advance receipt containing the tax information.
(I) Information for the current month
- 10A. Enter the advance amount information for reverse charge supplies for the current tax period, separately for interstate and intrastate supplies. The tax amount will be added to the output liability
- 10B. The details of advance amount on which tax has already been paid in earlier month/s but the invoice has been received just now, as given in table 4 above
(II) It will contain the revised information based on the changes made in the Part I information in an earlier tax period.
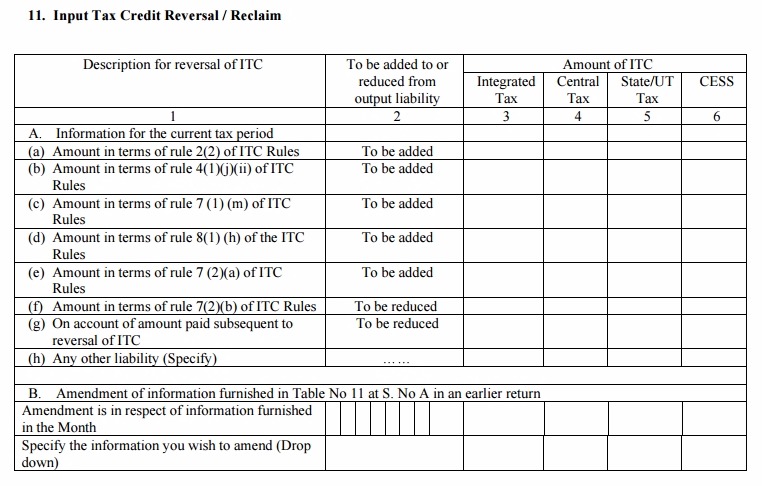
Table 11: Input Tax Credit Reversal/ Reclaim
- The details of input tax credit claims and reversals will be added to this table along with the amendment details if any
- ITC cannot be claimed on the non-business supplies of goods and services and for ITC exempt supplies
A. The details of ITC reclaims/reversals for the current month and that of exempt and personal supplies will be furnished in the head 11A.
- The amount in terms of rule 37(2) – ITC for invoices which were not paid within 180 days of issues will be reversed
- The amount in terms of rule 39(1)(j)(ii) – If the seller issues a credit note to the HO, the ITC reduced on the ISD will be reversed
- The amount in terms of rule 42(1)(m) – The ITC availed on non-business supplies will be reversed back
- The amount in terms of rule 43(1)(h) – ITC on non-business supplies of capital goods will be reversed proportionately
- The amount in terms of rule 42 (2)(a) – If the ITC availed on inward supplies of exempted/non-business goods is more than the actual ITC reversed after the annual return is filed, the difference will have to be paid along with the output tax liability
- The amount in terms of rule 42(2)(b) – For conditions opposite of the above, the difference between the ITC reversed and the ITC claimed will be available to be reclaimed
B. The user will have to manually enter the details of the changes in the information provided in Table 11A of the earlier tax periods.
Table 12: Addition and Reduction of the amount in output tax for mismatch and other reasons
- The details of additional tax liability due to mismatch or due to correction of the mismatch when filling GSTR-3 for the preceding tax period
- ITC claimed on mismatched/duplication of invoices/debit notes: If there was a mismatch in invoices and double ITC was claimed thereof, the excess ITC will be reversed
- Tax liability on mismatched credit notes: If extra ITC was claimed due to a mismatch in credit notes, it will be reversed and added to output tax liability
- Reclaim on account of rectification of mismatched invoices/debit notes: If lower ITC was claimed as a result of a mismatch in invoices, the additional ITC will be reduced from the tax liability
- Reclaim on account of rectification of mismatched credit note (Reduce): If lower ITC was claimed due to a mismatch in credit notes, the additional ITC will be available to the user
- Negative tax liability from previous tax periods: If the excess tax was paid in earlier months, it will be reduced from the current tax liability
- Tax paid on the advance in earlier tax periods and adjusted with tax on supplies made in current tax period (Reduce): Tax paid on advance payments received in earlier months but supplies received in this month
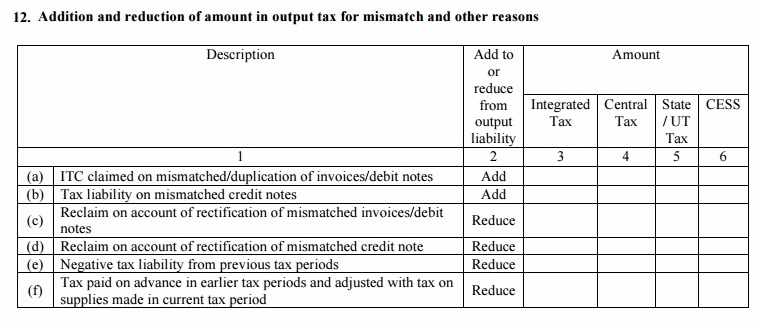
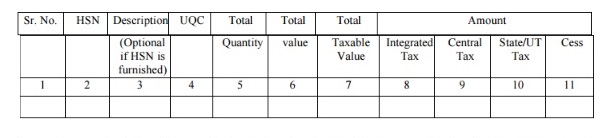
Table 13: HSN summary of inward supplies
- Summary of inward supplies along with proper HSN codes will be written in this table
Problems In Filing The GSTR-2 Form
Filing GST returns is not at all an easy task. Although the last date has been extended by the government, total taxpayer return filing estimate is still lower due to technical problems faced on the common portal.
Particular amendments in the GST rates and regulations are other factors which impacted the GST return filing. The GSTR-2 for July month is required to be filled by October 31 with the purchasing details by importers. The due date for GSTR-1 filing was 10 October with sales transaction details.
For input tax credit details, the GSTR-2 plays a very important role. Businesses can get easy refunds on the basis of filing and completeness of the GSTR-2 form. The GSTR-2 again matched with the one’s vendor.
The quick processing of refund mechanism is important as the taxpayer can fulfill their working capital requirements. For the first time working on this refund mechanism will drop a hope of confidence in the system, if the system goes well while filing returns.
The experience with GSTR-2 filing is better than GSTR-1, the reasons are obvious software issues while filing the GSTR-1.
Krishan Arora, a partner, Grant Thornton India, said that in GSTR-1 filing people were reporting the cases like invoices were confirmed but did not reflect in the auto-populated fields of the GSTR-2.
He also afraid about the people whose money is stuck and they have not filed the GSTR-1 yet. No changes can be made to typographical errors made in invoice number and invoice date on GSTN portal. The correct way to modify is to reject the invoice details and include correct details under “missing invoice” heads. This is a time-consuming process though.
The need of manual amendments in GST form filing is making the process hectic. In case if the taxpayer misses out the return uploading procedure, then the buyer is liable to make changes in GSTR-2 form by himself/herself.
The situations, being faced in the GSTR-2 filing, indicate no stability in the cash flow for traders. The first cycle for GST return filing including GSTR-1, GSTR-2, and GSTR-3 is going to end on 10 November and there is no surety of the Refund procedure.
It is necessary for the GST to gain flexibility and better implementation to make people happy about GST regime. GST is the biggest indirect tax reform after independence and expectations are quite high as it removes cascading effects. MS Mani, the partner at Deloitte India, said, “Since the overall concept of invoice matching on a monthly basis is new to all businesses and requires considerable efforts, it would be appreciated if the tax authorities take a sympathetic view to errors and omissions during the first six months.”










If we take less credit benefits for purchase and now in annual gstr2A shows more. Can we take benefit of that credit in GSTR9? And which column we need to made changes ?
In a recent notification issued by the department, you can claim ITC of FY 17-18 in returns(GSTR 3B) upto March 2019 provided that the ITC claimed should match with GSTR-2A. Further You’ll show it in GSTR-9 point 13.
Help for GST
Sir, my GSTR-2 has been submitted but not filed, while filing the same with OTP sent on my mobile, there is an error shown, to check the time on GST website. How do I file the GSTR-2 after submission?
Contact the department for assistance
Dear Sir, If by mistake some of the bills which have not been met by the importer but being entered by the supplier erroneously and which are auto-populated then what is the remedy available. (eg. LR payments)
Shall I accept the party invoice detail in july17 Gstr2 but actually we paid on August & shown in Aug17 Gstr 3 as Itc
As you have claimed it in GSTR-3 of August month, you need to reject it in July and also your dealer needs to reject it when it has shown in GSTR-1A of the dealer and then you both need to show it in next month’s GSTR -1/2 in the column of previous return data.
GSTR 2 status showing error in submission, I have furnished detail of 3,4A but not filled no 13 i.e HSN summary of inward supplies. Why error in submission showing and if we have turnover under 1.5 crores do we need to fill HSN summary of inward supplies section?
There might be some technical error. Please contact the department for assistance.
If we wrongly take CGST and SGST input in IGST and file gst3b then how to show in gstr2 and how to correct the same?
You can correct the same while filing GSTR1 and GSTR 2 for the month by filing the correct actual data in the return.
The supplier has FILED his GSTR-1, but recipient not able to take any action against that Invoice in GSTR-2. The supplier has “FILED” Status for GSTR-1. Can you please elaborate the Same?
Entries done by the supplier in GSTR 1 will be reflected in GSTR 2A of the receiver for approval so the receiver can approve or disapprove the entries reflected in GSTR 2A and can file his GSTR 2.
Some of the input shows in 2A & also 2 but it won’t accept or reject or delete as they not submitted.shall I take addition & take no action & submit 2 is it possible.
Please add busy support too. Not everyone uses tally. Also, make import and export of Excel and JSON files easy.
Dear Sir, for your reply to HSN wise detail in GSTR 2 GSTN portal site is not accepting detail of exempted goods. They accept only detail of taxable goods. Is it not necessary to mention the detail of exempted goods.
Is it necessary for HSN summary of inward supplies?
Dear Sir, GSTR-2 HSN summary is not accepting of goods exempted. Please advice only taxable goods should be feed with thanks
No such bar has been placed on mentioning hsn code only for the taxable goods.
Dear sir, I am not clear for RCM please advice me from recent notification for which expenses I have not to pay rcm. I am a registered dealer under GST. I am paying daily transport charges to the unregistered transporter for purchasing of goods. Also, i pay shop rent 18000 per month. Please clear my doubt.
with thanks
RCM has been suspended only for the supplies from unregistered persons. If you are availing GTA service from a registered provider then, RCM provisions will be applicable to you. If your landlord is not registered under GST then RCM provisions are not applicable.
I want to claim CST paid on the stock as on 30-6-2017, whether I have to file trans 1 or trans 2 and in which part of the return.
The credit of CST is not allowed to be carried forward under GST. Only those amounts can be carried the forward credit of which is allowed under the previous law.
In case my invoices in GSTR 2 is more for accepting and rejecting… do they have excel schema to export the 2a data into excel and modify the same and upload it again.
Do we have to fill HSN details for inward supplies if turnover is less than 1.5 CRORE
Yes, you have to give HSN detail in HSN summery column for inward supplies.
Do we have to enter HSN details manually in GSTR 2 as it is not getting auto-populated in GSTR 2…???
You have to manually enter the HSN summary.
How to find the bill of entry on DHL or FedEx invoice in case of import of goods by air parcel?
BUT HOW TO DO IT ONLINE?????